Individual Tree Detection (ITC)
From AWF-Wiki
(Difference between revisions)
(→Watershed segmentation) |
(→Filter the CHM derived from LiDAR data) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
=Filter the CHM derived from LiDAR data= | =Filter the CHM derived from LiDAR data= | ||
| − | We use a Canopy Height Model (CHM) derived from LiDAR data as decribed [http://wiki.awf.forst.uni-goettingen.de/wiki/index.php/Canopy_Height_Model_based_on_Airborne_Laserscanning_using_LAStools#Create_a_CHM_directly_from_height-normalized_points:_lasthin_and_las2dem here] to detect | + | We use a Canopy Height Model (CHM) derived from LiDAR data as decribed [http://wiki.awf.forst.uni-goettingen.de/wiki/index.php/Canopy_Height_Model_based_on_Airborne_Laserscanning_using_LAStools#Create_a_CHM_directly_from_height-normalized_points:_lasthin_and_las2dem here] to detect Individual Tree Crowns (ITC). |
Two preprocessing steps prepare a watershed segmentation approach: (1) Gaussian filtering and (2) inversion of a CHM. | Two preprocessing steps prepare a watershed segmentation approach: (1) Gaussian filtering and (2) inversion of a CHM. | ||
* In the search engine of the Processing Toolbox, type {{typed|text=smooth}} and select '''Smoothing (gaussian)''' under Image filtering of the Orfeo Toolbox. | * In the search engine of the Processing Toolbox, type {{typed|text=smooth}} and select '''Smoothing (gaussian)''' under Image filtering of the Orfeo Toolbox. | ||
Revision as of 23:43, 6 January 2018
Contents |
Filter the CHM derived from LiDAR data
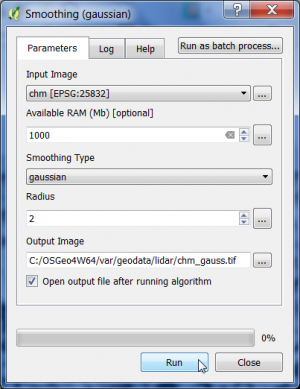
We use a Canopy Height Model (CHM) derived from LiDAR data as decribed here to detect Individual Tree Crowns (ITC). Two preprocessing steps prepare a watershed segmentation approach: (1) Gaussian filtering and (2) inversion of a CHM.
- In the search engine of the Processing Toolbox, type smooth and select Smoothing (gaussian) under Image filtering of the Orfeo Toolbox.
- Select the CHM raster data file in GeoTiff format as input layer.
- The smoothing type is gaussian.
- The circular structuring element has a radius of 2 pixels.
- Enter name and path for an output file.
- Click on Run.
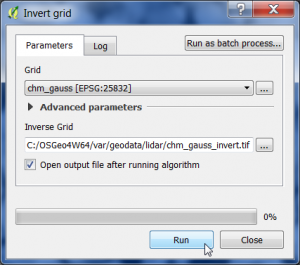
Invert the CHM
Now the smoothed CHM will be inverted.
- In the search engine of the Processing Toolbox, type invert and select Invert grid under Raster tools of SAGA.
- Select the smoothed CHM raster data file from previous step as input layer.
- Enter name and path for an output file.
- Click on Run.
Watershed segmentation
- In the search engine of the Processing Toolbox, type watershed and select Watershed segementation under Image Analysis of SAGA.
- Select the inverted and smoothed CHM raster data file as input Grid.
- The Output is Segment ID
- Select as Method the flow accumulation of Minima
- Seed points: enter name and path for a vector point output file.
- Click on Run.