Individual Tree Detection (ITC)
From AWF-Wiki
(Difference between revisions)
(→Extracting tree heights) |
(→Extracting tree heights) |
||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
* Toggle editing on. | * Toggle editing on. | ||
* Select features using an expression. | * Select features using an expression. | ||
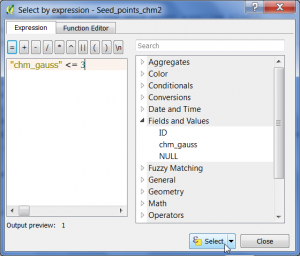
| − | * Type in the expression editor: {{typed|text="chm" <= 3}} and click {{button|text=Select}}. All | + | * Type in the expression editor: {{typed|text="chm" <= 3}} and click {{button|text=Select}}. All points with heights below 3m are now selected. |
* Click '''Delete selected features'''. | * Click '''Delete selected features'''. | ||
* Toggle editing off. | * Toggle editing off. | ||
Revision as of 13:21, 7 January 2018
Contents |
Filter the CHM derived from LiDAR data
We use a Canopy Height Model (CHM) derived from LiDAR data as decribed here to detect Individual Tree Crowns (ITC). Two preprocessing steps prepare a watershed segmentation approach: (1) Gaussian filtering and (2) inversion of a CHM.
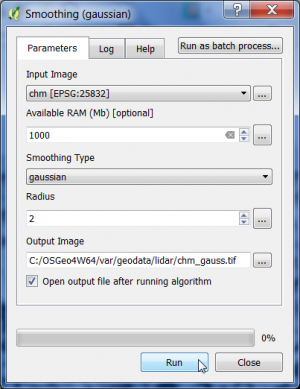
- In the search engine of the Processing Toolbox, type smooth and select Smoothing (gaussian) under Image filtering of the Orfeo Toolbox.
- Select the CHM raster data file in GeoTiff format as input layer.
- The smoothing type is gaussian.
- The circular structuring element has a radius of 2 pixels.
- Enter name and path for an output file.
- Click on Run.
Invert the CHM
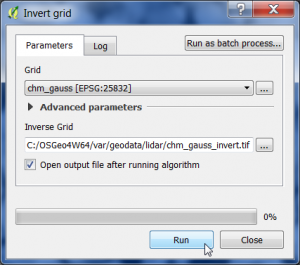
Now the smoothed CHM will be inverted.
- In the search engine of the Processing Toolbox, type invert and select Invert grid under Raster tools of SAGA.
- Select the smoothed CHM raster data file from previous step as input layer.
- Enter name and path for an output file.
- Click on Run.
Watershed segmentation
- In the search engine of the Processing Toolbox, type watershed and select Watershed segementation under Image Analysis of SAGA.
- Select the inverted and smoothed CHM raster data file as input Grid.
- The Output is Segment ID
- Select as Method the flow accumulation of Minima
- Seed points: enter name and path for a vector point output file.
- Click on Run.
Extracting tree heights
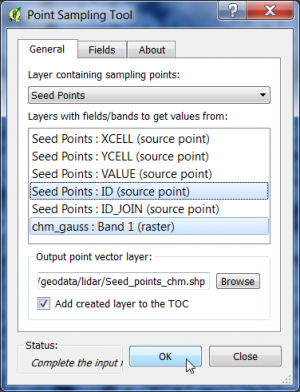
We extract normalized heights from the original CHM using the QGIS point sampling plugin.
- Click Plugins --> Manage and Install Plugins.
- Type in the search bar Point sampling tool, click on the plugin name and then on Install plugin.
- Load the single band raster file chm.tif.
- Load the vector point file Seed points.shp'.
- Make sure that both layers are ticked in the TOC.
- Open the Point Sampling Tool clicking
 .
.
- Specify the output of the resulting vector file marking column with CTRL + left click.
- Enter an output shapefile name seed_points_chm.shp and path by clicking Browse.
- Confirm with OK. The new layer is added to the Layer Panel .
- Right click on the layer name in the TOC and open the Attribute table of the new vector layer.
- Toggle editing on.
- Select features using an expression.
- Type in the expression editor: "chm" <= 3 and click Select. All points with heights below 3m are now selected.
- Click Delete selected features.
- Toggle editing off.
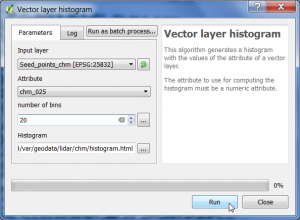
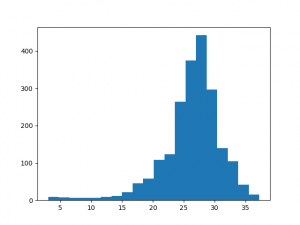
- In the search engine of the Processing Toolbox, type histogram and select Vector layer histogram under Graphics of QGIS geoalgorithms.
- Select the shapefile name seed_points_chm.shp as input layer.
- Select as Attribute the column with the extracted height values chm.
- Select the number of histogram bins20.
- Enter name and path for a graphic output file.
- Click on Run.