Supervised classification (Tutorial)
| Line 58: | Line 58: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | [[ | + | [[Category:QGIS Tutorial 2013/14]] |
Revision as of 12:24, 26 February 2014
| sorry: |
This section is still under construction! This article was last modified on 02/26/2014. If you have comments please use the Discussion page or contribute to the article! |
- This article is part of the QGIS tutorial 2013/14.
In this article, you will learn how to conduct a supervised image classification in QGIS 2.0
Contents |
Plugin installation and testing
- Installing the plugin.
- Click Manage and install plugins.
- In the appearing menu, select Add more.
- Browse for the Semi-Automatic Classification Plugin (it's most comfortable to use the search-field).
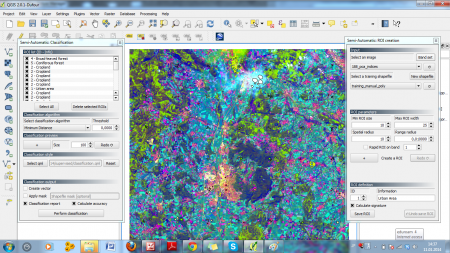
- Click Install. If installation was successful, two additional windows should add to the QGIS GUI (Classification and ROI creation, see figure A).
- Testing the plugin
- For the plugin to work, you need to make sure that your installations of GRASS GIS, ORFEO Toolbox and SAGA GIS work correctly.
- With the plugin installed, select Raster --> Semi Automatic Class Plugin.
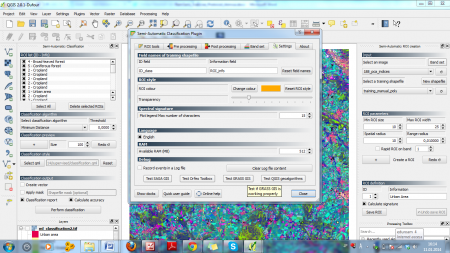
- In the appearing menu, select the Settings tab (figure B). Click Test Grass GIS and wait until the message Test OK appears. Do the same the Orfeo Toolbox, Saga and Qgis geoalgorithms.
Classification
- Add the raster map 188_pca_indices.tif from the course data (see previous exercises).
- Also add the vector layer Training_manual_poly.shp.
ROI digitalization
For better understanding of the workflow, try digitizing some Regions Of Interest yourself.
- First, you need to create a new shapefile to store the ROIs.
- In the Input section of the ROI creation menu, click the New shapefile button. Just select the directory and file for the new shapefile and add it to the canvas. Click the Refresh list of shapefiles button and select your shapefile from the pulldown menu.
- In the ROI Definition section you can add define the attributes of each ROI. The Macroclass ID, which may be used to code sub-classes of the main classes (like e.g. Coniferous forest as a macroclass of Forest), the Class ID and the name of the class in the Information column.
- As an example, enter Urban area in the Information column and leave the ID's as they are.
- Looking at the ROI creation section, you see two options for generating the ROI:
- By clicking +, you can select nondimensional points at the map. Simply place them in pixel clusters you have identified as belonging to the respective class. The regions will later be generated by region growing.
- A more precise way is to delineate ROI polygons using the Create a ROI polygon tool. You can re-draw the shape of a specific pixel cluster on the map and finish with a right-click.
- After having digitized a certain number of points or polygons for a ROI, click Save ROI. Wait until the computation is finished. You will then see the ROI being added to the ROI list in the Classification window.
- Repeat ROI generation for a few classes, like e.g.
- Forest
- Agricultural area
- Water
- Clouds
- After having added a few classe, select Minimum distance in the Classification algorithm section. Click + in the Classification preview section. By clicking somewhere on the map, a small preview for a section of the map will be generated.
Using predefined ROIs
Just adding a few classes will not generate a satisfying classification result. For a high quality classification, ROIs have to be very well defined, which requires a lot of time. For a supervised classification closer to real-life, you can use some predefined ROIs.
- Load the shapefile training_manual_poly.shp into the project and select it as training shapefile. You'll see how the ROI list is automatically updated.
- For Classification style click Select qml and browse for the file classification.qml from the course data.
- In the Classification output section, check the Classificatin report and Calculate accuracy boxes.
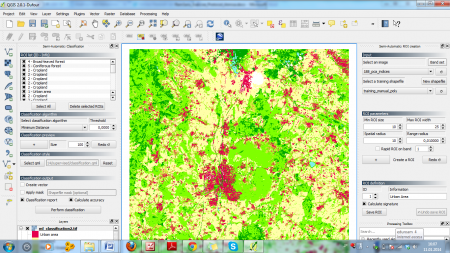
- Click Perform classification. Enter name and path for the output map (e.g. ml_classification.tif) and wait for the classification to finish (figure C). This may take a long time! Plan to do some different work (or just have lunch) while the algorithm is running.
Alternative algorithms and accuracy assessment
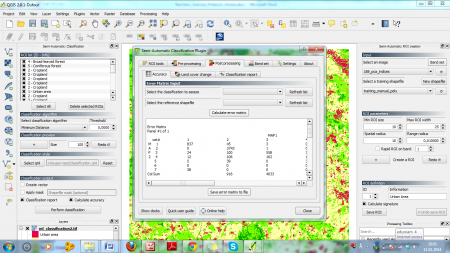
To get an impression of results depending on the alorithm selected, try the Maximum likelihood classifier as Classification algorithm. In the Semi Automatic classification dialogue (figure D), select the Post processing tab to view the error matrix. If desired, it can be saved for future reference.