Forest boundary
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Ficontent}} | {{Ficontent}} | ||
| − | |||
[[File:2.1.4-fig8.png|left|thumb|285px|'''Figure 1''' Some definitions of forest boundary. (Kenneweg 2002<ref name="kenneweg2002">Kenneweg, H. 2002. Neue methodische Ansätze zur Fernerkundung in den Bereichen Landschaft, Wald und räumliche Planung. In: Dech S et al. (Hrsg.): Tagungsband 19. DFD-Nutzerseminar, 15.-16. Okt. 2002, S. 127-137. </ref>).]] | [[File:2.1.4-fig8.png|left|thumb|285px|'''Figure 1''' Some definitions of forest boundary. (Kenneweg 2002<ref name="kenneweg2002">Kenneweg, H. 2002. Neue methodische Ansätze zur Fernerkundung in den Bereichen Landschaft, Wald und räumliche Planung. In: Dech S et al. (Hrsg.): Tagungsband 19. DFD-Nutzerseminar, 15.-16. Okt. 2002, S. 127-137. </ref>).]] | ||
| Line 7: | Line 6: | ||
Even if there is an abrupt change from forest to, for example, agriculture, one must still define whether the vertical projection of the crowns is the forest boundary (that is relatively easy to determine from aerial photographs) or the connecting line between the stems at the forest edge (that is easily be done in the field). Figure 1 illustrates various options. | Even if there is an abrupt change from forest to, for example, agriculture, one must still define whether the vertical projection of the crowns is the forest boundary (that is relatively easy to determine from aerial photographs) or the connecting line between the stems at the forest edge (that is easily be done in the field). Figure 1 illustrates various options. | ||
| − | In particular in highly [[fragmented]] forested landscapes, where the length of the forest boundary is considerable, the question of definition of forest boundary is important; different definitions can considerably alter the [[Minimum crown cover|forest cover]] estimates: if the crown projection is taken as forest boundary, the forest area will be larger compared to a forest boundary that goes along the connecting line between border [[Tree Definition|stems]]. | + | In particular in highly [[fragmented]] forested landscapes, where the [[Estimating the length of the forest edge|length of the forest boundary]] is considerable, the question of definition of forest boundary is important; different definitions can considerably alter the [[Minimum crown cover|forest cover]] estimates: if the crown projection is taken as forest boundary, the forest area will be larger compared to a forest boundary that goes along the connecting line between border [[Tree Definition|stems]]. |
Again, there is no “right” or “wrong” definition, but only “clear” and “not-clear” definitions. There are only few forest inventories that contain a clear and operational definition of where the forest boundary exactly is. | Again, there is no “right” or “wrong” definition, but only “clear” and “not-clear” definitions. There are only few forest inventories that contain a clear and operational definition of where the forest boundary exactly is. | ||
Revision as of 16:37, 27 October 2013
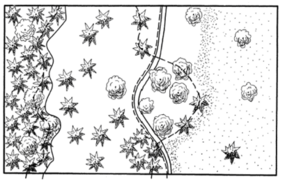
When defining forest, one must also define where forest ends; forest edge or forest boundary is the imagined line that separates forest and non-forest. The question of a clear definition of the forest boundary is particularly difficult in transition areas between forest and non-forest where a dense forest is gradually opening up to tree-free land, as for example at the timber line or at the boundary of deserts (Kleinn 2007[2]).
Even if there is an abrupt change from forest to, for example, agriculture, one must still define whether the vertical projection of the crowns is the forest boundary (that is relatively easy to determine from aerial photographs) or the connecting line between the stems at the forest edge (that is easily be done in the field). Figure 1 illustrates various options.
In particular in highly fragmented forested landscapes, where the length of the forest boundary is considerable, the question of definition of forest boundary is important; different definitions can considerably alter the forest cover estimates: if the crown projection is taken as forest boundary, the forest area will be larger compared to a forest boundary that goes along the connecting line between border stems.
Again, there is no “right” or “wrong” definition, but only “clear” and “not-clear” definitions. There are only few forest inventories that contain a clear and operational definition of where the forest boundary exactly is.
References
- ↑ Kenneweg, H. 2002. Neue methodische Ansätze zur Fernerkundung in den Bereichen Landschaft, Wald und räumliche Planung. In: Dech S et al. (Hrsg.): Tagungsband 19. DFD-Nutzerseminar, 15.-16. Okt. 2002, S. 127-137.
- ↑ Kleinn, C. 2007. Lecture Notes for the Teaching Module Forest Inventory. Department of Forest Inventory and Remote Sensing. Faculty of Forest Science and Forest Ecology, Georg-August-Universität Göttingen. 164 S.