Canopy Height Model based on Airborne Laserscanning using LAStools
Contents |
Download of LAStools
LASTools is software for efficient processing of LiDAR data (Laser scanning data) programmed by rapidlasso GmbH. There are two parts of LAStools: one part is Open Source (LGPL 2.1), the other part is Closed Source and requires licensing for most commercial or government uses. The closed source software may be used without charge for non-profit personal, non-military educational, or non-profit humanitarian purposes. Note, that the output of the unlicensed version can be slightly distorted after certain point limits (1 million points) are exceeded. Download the recent version as LAStools.zip file. Extract the zip file to a folder without space (e.g. C:\LAStools).
Configure Tools for LiDAR data in QGIS Processing Toolbox
Start QGIS.
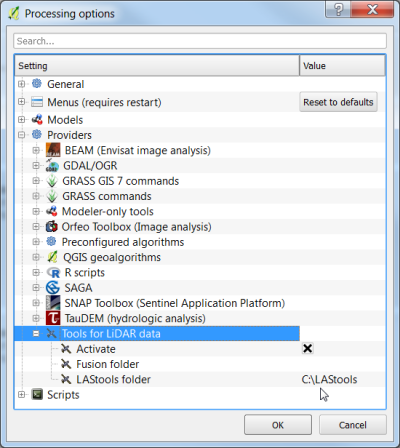
Open Processing --> Options --> Providers --> Tools for LiDAR data.
Check the Activate button and fill in the path to your local LAStools folder as shown below.
Point cloud visualization: lasview
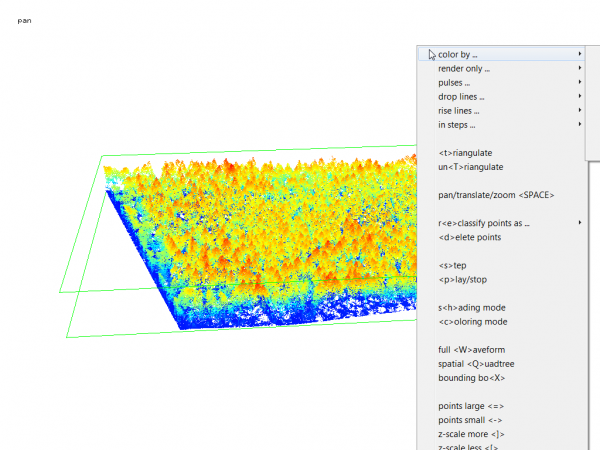
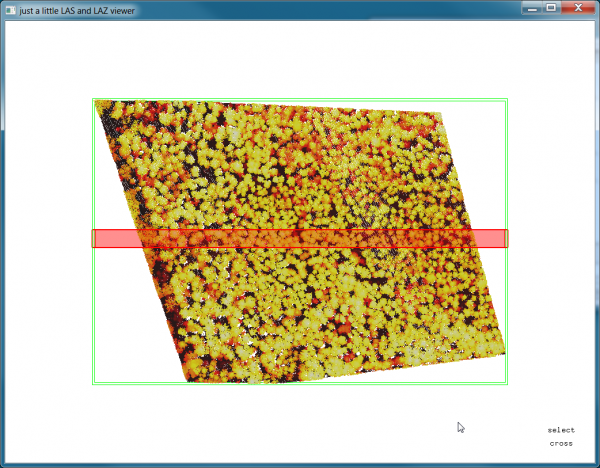
lasview is an OpenGL-based viewer for LiDAR in LAS/LAZ/ASCII format that can also edit or delete points as well as compute/display a TIN computed from (a selection of) points.
- In the search engine of the Processing Toolbox, type lasview and select lasview under LAStools of the Tools for LiDAR data.
- Select a LiDAR data file in LAZ format as the input layer.
- Select color by elevation2 from the drop down list.
- Click on Run to start the viewer.
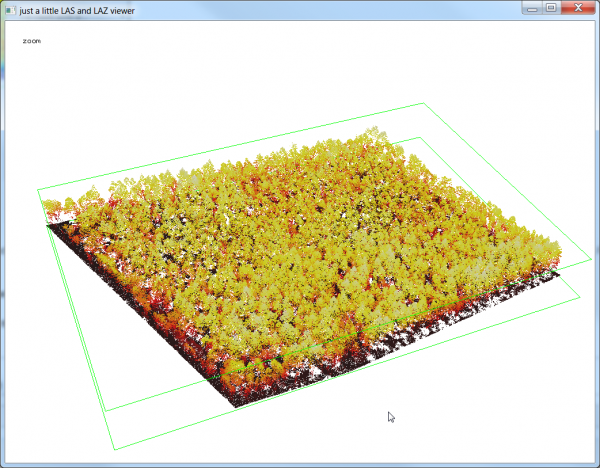
- The viever will open in PAN mode. Left click and hold moving the cursor to rotate the point cloud. Press the space bar to switch to TRANSLATE or ZOOM mode and change the perspective interactively. Open the context menu with a right click to see other functions of lasview as seen below.
- Type <c> to try other color maps.
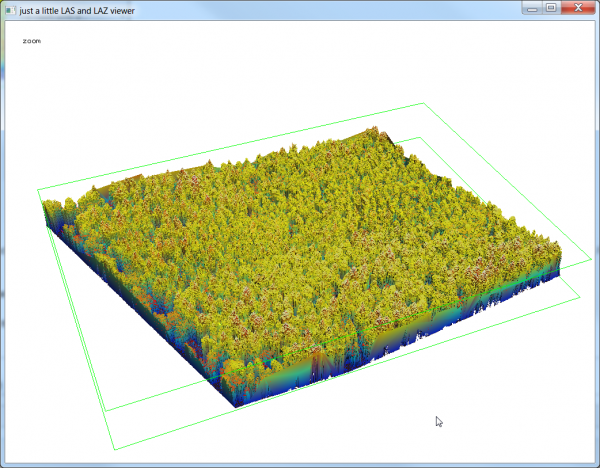
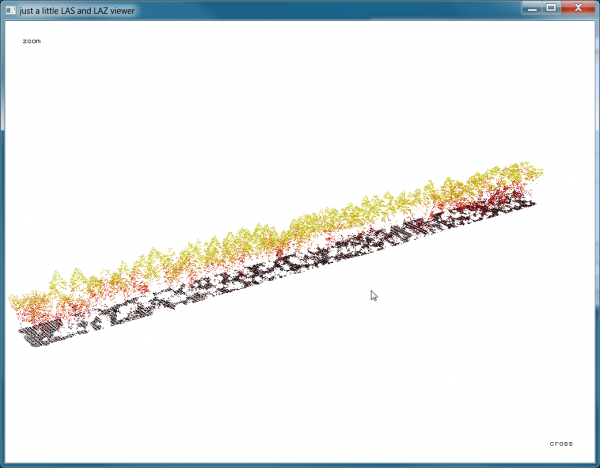
- Type <t> to create a TIN.
- Type <h> to try different shadings of the TIN.
- Type <T> to return back to the point cloud view.
- For quality checking and detail views you can press <x> and select a cross section or smaller area of interest. Move it around with the arrow key. Holding down <SHIFT> or <ALT> is taking larger or smaller steps.
- Press <x> again and you see only the selected area.
- Jump back between cross section view and the full extend with <x>.
- Type <X> to switch the green bounding box off or on.
- You can also edit the classification of the points as well as delete them. For more details see the README file in the C:\LAStools\bin folder or open the context menu with a right mouse click on the viewer.
Point cloud metadata: lasinfo
lasinfo reports the contents of the file header and a short summary of the points such as point density and spacing.
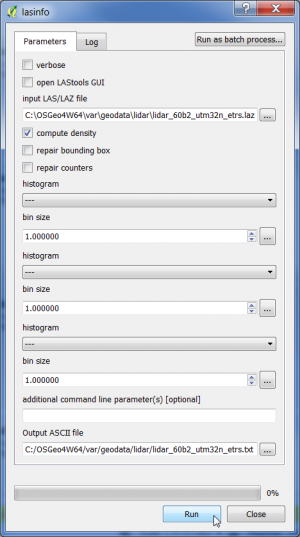
- In the search engine of the Processing Toolbox, type lasinfo and select lasinfo under LAStools of the Tools for LiDAR data.
- Select a LiDAR data file in LAZ format as the input layer.
- Check the Compute density button.
- Enter name and path for the output text file.
- Click on Run.
- Open the output file with an text editor an report the most important LiDAR data characteristics:
- Which Coordinate Reference System is defined?
- What is the point density?
- What is the point spacing?
Extracting digital terrain model: lasground
lasground is a tool for bare-earth extraction: it classifies LIDAR points into ground points (class = 2) and non-ground points (class = 1).
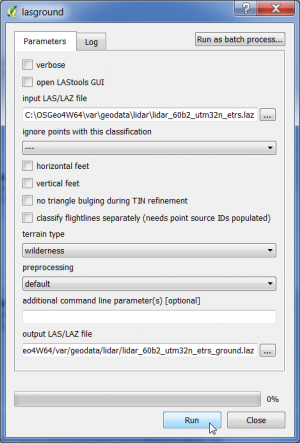
- In the search engine of the Processing Toolbox, type lasground and select lasground under LAStools of the Tools for LiDAR data.
- Select a LiDAR data file in LAZ format as the input layer.
- Select as terrain type wilderness.
- Select default preprocessing.
- Enter name and path for the classified output file.
- Click on Run.