Unsupervised classification (Tutorial)
From AWF-Wiki
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
* Load the resulting image into QGIS. It is single band file with 20 grey levels labeled from 0 to 19. | * Load the resulting image into QGIS. It is single band file with 20 grey levels labeled from 0 to 19. | ||
* {{mitem|text=Layer Properties --> Symbology --> Render type}}. Switch to {{button|text=Singleband pseudocolor}} and select a '''Color ramp''' (e.g. Spectral). Select the '''Mode''' {{button|text=Equal interval}} and set the number of classes to {{typed|text=20}} | * {{mitem|text=Layer Properties --> Symbology --> Render type}}. Switch to {{button|text=Singleband pseudocolor}} and select a '''Color ramp''' (e.g. Spectral). Select the '''Mode''' {{button|text=Equal interval}} and set the number of classes to {{typed|text=20}} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Latest revision as of 14:37, 24 November 2020
[edit] Unsupervised K-Means classification
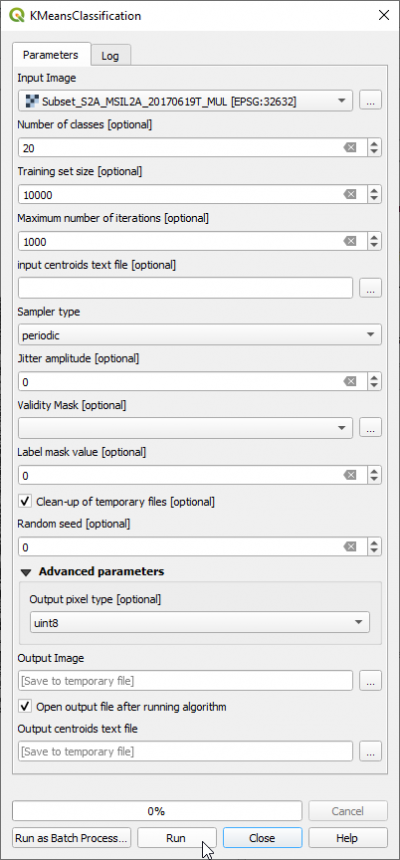
- In the search engine of the Processing Toolbox, type kmeans and double click KMeansClassification of OTB.
- Specify a multispectral image as Input Image.
- Specify directory and name for the Output image. Select the output data type uint 8 from the pull-down list.
- Set the Number of classes to 20
- Check the Training set size to 10000
- Output pixel type: uint8
- Click on Run.
- Load the resulting image into QGIS. It is single band file with 20 grey levels labeled from 0 to 19.
- Layer Properties --> Symbology --> Render type. Switch to Singleband pseudocolor and select a Color ramp (e.g. Spectral). Select the Mode Equal interval and set the number of classes to 20