Image fusion
From AWF-Wiki
(Difference between revisions)
(Created page with "= Create a superimposed layer (reprojected image) = # Add the panchromatic band 8 (15m GSD) and multispectral bands (B1 – B7, 30m GSD) into QGIS using the ‘add raster laye...") |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | Pansharpening of Sentinel-2 requires defining a 10m reference band because there is no panchromatic band as for Landsat available. The only option is a selection among the 10-m bands (2, 3, 4, or 8) or synthesis (e.g. weighted average of 10-m band). Following the latter approach, the luminance can be calculated from the Blue, Red Green and NIR band to receive a single band grey scale image. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | = Create a synthesis panchromatic band = | |
| − | # | + | # Load the input image |
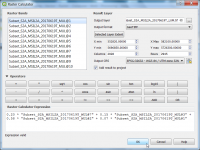
| − | # | + | # Open the raster calculator and apply the following formula: Y = 0.20 * NIR(B8) 0.15 * Red(B4) + 0.58 * Green(B3) + 0.07 * Blue(B1) |
| − | # | + | [[File:rastercalc.png|200px]] |
| + | # Define path and name for the output layer | ||
| + | # Click on the ‘OK-button’. | ||
= Create a pan-sharpened layer = | = Create a pan-sharpened layer = | ||
# Search for Pansharpening (Bayes) algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. | # Search for Pansharpening (Bayes) algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. | ||
| − | # Select | + | # Select pseudo-panchromatic band as the Input PAN Image. |
| − | # Select the | + | # Select the layer contain the original 20m bands as the InputXS Image. |
# Specify the directory to save the output file and click on the ‘Run-button’. | # Specify the directory to save the output file and click on the ‘Run-button’. | ||
= Compare the fused image with the original image = | = Compare the fused image with the original image = | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | [[File:no_pansharpen.png|400px]] [[File:pansharpen.png|400px]] | ||
[[Category:QGIS Tutorial]] | [[Category:QGIS Tutorial]] | ||
Revision as of 18:45, 16 November 2017
Pansharpening of Sentinel-2 requires defining a 10m reference band because there is no panchromatic band as for Landsat available. The only option is a selection among the 10-m bands (2, 3, 4, or 8) or synthesis (e.g. weighted average of 10-m band). Following the latter approach, the luminance can be calculated from the Blue, Red Green and NIR band to receive a single band grey scale image.
Create a synthesis panchromatic band
- Load the input image
- Open the raster calculator and apply the following formula: Y = 0.20 * NIR(B8) 0.15 * Red(B4) + 0.58 * Green(B3) + 0.07 * Blue(B1)
- Define path and name for the output layer
- Click on the ‘OK-button’.
Create a pan-sharpened layer
- Search for Pansharpening (Bayes) algorithm in the Processing Toolbox.
- Select pseudo-panchromatic band as the Input PAN Image.
- Select the layer contain the original 20m bands as the InputXS Image.
- Specify the directory to save the output file and click on the ‘Run-button’.