Digitizing training and test areas
From AWF-Wiki
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
:''This article is part of the [[QGIS tutorial 2013/14]].<br/>In this article you will learn how to create test areas for landscape classification.'' | :''This article is part of the [[QGIS tutorial 2013/14]].<br/>In this article you will learn how to create test areas for landscape classification.'' | ||
| Line 9: | Line 7: | ||
## Set {{button|text=Initial set from corner (LH side)}} | ## Set {{button|text=Initial set from corner (LH side)}} | ||
## Enter the file name and path by clicking {{button|text=Browse}}. You may use ''188_pca_indices_points'' as a file name. | ## Enter the file name and path by clicking {{button|text=Browse}}. You may use ''188_pca_indices_points'' as a file name. | ||
| − | ## Confirm with {{button|text=OK}}. Let the new layer be added to the [[TOC]]. | + | ## Confirm with {{button|text=OK}}. Let the new layer be added to the [[TOC]] (figure '''A'''). |
##* If the points are hard to recognize on the [[QGIS GUI|canvas]], open the properties by double-clicking the layer in the [[TOC]] and adjusting size and color in the {{button|text=Style}} tab. | ##* If the points are hard to recognize on the [[QGIS GUI|canvas]], open the properties by double-clicking the layer in the [[TOC]] and adjusting size and color in the {{button|text=Style}} tab. | ||
# Buffering sample points | # Buffering sample points | ||
## Open {{mitem|text=Vector --> Geoprocessing tools --> Buffer}}. Select the generated points shapefile as input layer. | ## Open {{mitem|text=Vector --> Geoprocessing tools --> Buffer}}. Select the generated points shapefile as input layer. | ||
## Enter 200 (meter) as {{mitem|text=Buffer distance}}. | ## Enter 200 (meter) as {{mitem|text=Buffer distance}}. | ||
| − | ## Enter a file path and name, e.g. ''188_pca_indices_buffer'', confirm with {{button|text=OK}} and confirm the following dialogue to let the result be added to the project. | + | ## Enter a file path and name, e.g. ''188_pca_indices_buffer'', confirm with {{button|text=OK}} and confirm the following dialogue to let the result be added to the project (figures '''B'''). |
# To get an overview of the terrain, you may add a google sattelite layer | # To get an overview of the terrain, you may add a google sattelite layer | ||
| − | ## Select {{mitem|text=Plugins --> OpenLayers plugin --> Add Google Sattelite layer}}. Of course, you can also add a hybrid layer or try the layers from different providers. | + | ## Select {{mitem|text=Plugins --> OpenLayers plugin --> Add Google Sattelite layer}} (figure '''C'''). Of course, you can also add a hybrid layer or try the layers from different providers. |
##* If the Plugin doesn't exist in you [[QGIS]] installation, you'll first have to [[QGIS_plugin_administration|install]] it. | ##* If the Plugin doesn't exist in you [[QGIS]] installation, you'll first have to [[QGIS_plugin_administration|install]] it. | ||
# Create a new shapefile layer | # Create a new shapefile layer | ||
| Line 29: | Line 27: | ||
## Open the file ''digitizing_classes.pdf'' from the [[Course data|course data]] for a reference of landscape classes. | ## Open the file ''digitizing_classes.pdf'' from the [[Course data|course data]] for a reference of landscape classes. | ||
## Select the new shapefile in the [[TOC]]. Start the edit mode by clicking the {{button|text=Toggle editing}} button [[file:QGIS_2.0_Edit.png|25px]]. | ## Select the new shapefile in the [[TOC]]. Start the edit mode by clicking the {{button|text=Toggle editing}} button [[file:QGIS_2.0_Edit.png|25px]]. | ||
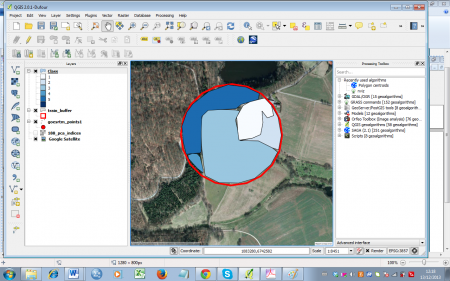
| − | ## Click {{button|text=Add feature}} [[file:QGIS_2.0_Addpolygon.png|25px]] to start digitizing. Draw polygons according to the landscape classes. Simply click the desired point on the canvas to start. After selecting a second point, the third point will construct a triangle and each additional point will add another triangle to the geometry. Finish the geometry by right-clicking and entering the attributes in the appearing window (just use an increasing number for the ID). Take your time to get used to this way of digitizing -- you can always delete the last polygon by simply clicking {{button|text=Cancel}} in the attributes dialogue, or by selecting it [[file:QGIS_2.0_Select.png|25px]] and deleting with the {{button|text=Delete selected}} [[file:QGIS_2.0_Delete_selected.png|25px]] button. | + | ## Zoom in on a sample point (figure '''D'''). Click {{button|text=Add feature}} [[file:QGIS_2.0_Addpolygon.png|25px]] to start digitizing. Draw polygons according to the landscape classes. Simply click the desired point on the canvas to start. After selecting a second point, the third point will construct a triangle and each additional point will add another triangle to the geometry. Finish the geometry by right-clicking and entering the attributes in the appearing window (just use an increasing number for the ID). Take your time to get used to this way of digitizing -- you can always delete the last polygon by simply clicking {{button|text=Cancel}} in the attributes dialogue, or by selecting it [[file:QGIS_2.0_Select.png|25px]] and deleting with the {{button|text=Delete selected}} [[file:QGIS_2.0_Delete_selected.png|25px]] button. An example of a finished sample point can be seen in figure '''E'''. |
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | | [[file:RemSens_Exercise06_01.png|thumb|450px|'''Figure A:''' Map ''188_pca_indices'' with sample points]] | ||
| + | | [[file:RemSens_Exercise06_02.png|thumb|450px|'''Figure B:''' Buffered sample points]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[file:RemSens_Exercise06_03.png|thumb|450px|'''Figure C:''' Google satellite layer loaded via the ''Open layers'' plugin]] | ||
| + | | [[file:RemSens_Exercise06_04.png|thumb|450px|'''Figure D:''' Zoom-in on buffered sample point with underlying Google satellite layer]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[file:RemSens_Exercise06_05.png|thumb|450px|'''Figure E:''' Example of a sample point after digitizing landscape classes]] | ||
| + | |} | ||
[[Category: QGIS exercises 2013/14]] | [[Category: QGIS exercises 2013/14]] | ||
Revision as of 18:22, 24 January 2014
- This article is part of the QGIS tutorial 2013/14.
In this article you will learn how to create test areas for landscape classification.
- Generating sample points
- Load the raster map 188_pca_indices, which should be available in the course data.
- Open Vector --> Research tools --> regular points. If not selected by default, set the Input Boundary Layer to 188_pca_indices.
- Select the radio button Use this number of points and set the number to 50.
- Set Initial set from corner (LH side)
- Enter the file name and path by clicking Browse. You may use 188_pca_indices_points as a file name.
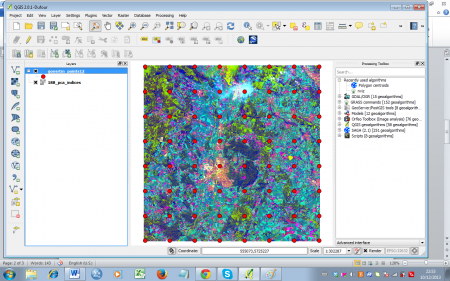
- Confirm with OK. Let the new layer be added to the TOC (figure A).
- Buffering sample points
- Open Vector --> Geoprocessing tools --> Buffer. Select the generated points shapefile as input layer.
- Enter 200 (meter) as Buffer distance.
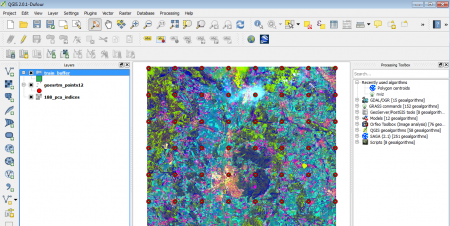
- Enter a file path and name, e.g. 188_pca_indices_buffer, confirm with OK and confirm the following dialogue to let the result be added to the project (figures B).
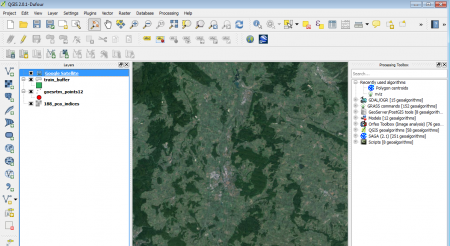
- To get an overview of the terrain, you may add a google sattelite layer
- Create a new shapefile layer
- Select Layer --> New --> New Shapefile Layer.
- As layer type, select Polygon. Click the Specify SRS button and select WGS 84/Pseudo Mercator (EPSG:3857).
- To add an attibute:
- For the attribute's name type (Class into the Name field of the New attribute section.
- Select Whole number as data type.
- Confirm with Add to attributes list.
- Confirm with OK and enter the path and name (e.g. Training) in the following menu.
- Select Layer --> New --> New Shapefile Layer.
- Digitizing areas
- Open the file digitizing_classes.pdf from the course data for a reference of landscape classes.
- Select the new shapefile in the TOC. Start the edit mode by clicking the Toggle editing button
 .
.
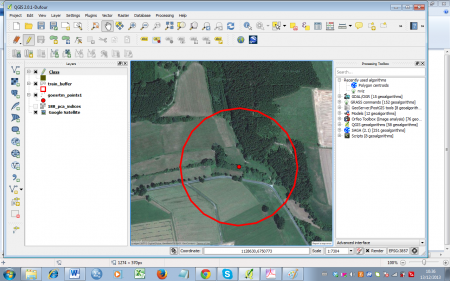
- Zoom in on a sample point (figure D). Click Add feature
 to start digitizing. Draw polygons according to the landscape classes. Simply click the desired point on the canvas to start. After selecting a second point, the third point will construct a triangle and each additional point will add another triangle to the geometry. Finish the geometry by right-clicking and entering the attributes in the appearing window (just use an increasing number for the ID). Take your time to get used to this way of digitizing -- you can always delete the last polygon by simply clicking Cancel in the attributes dialogue, or by selecting it
to start digitizing. Draw polygons according to the landscape classes. Simply click the desired point on the canvas to start. After selecting a second point, the third point will construct a triangle and each additional point will add another triangle to the geometry. Finish the geometry by right-clicking and entering the attributes in the appearing window (just use an increasing number for the ID). Take your time to get used to this way of digitizing -- you can always delete the last polygon by simply clicking Cancel in the attributes dialogue, or by selecting it  and deleting with the Delete selected
and deleting with the Delete selected  button. An example of a finished sample point can be seen in figure E.
button. An example of a finished sample point can be seen in figure E.