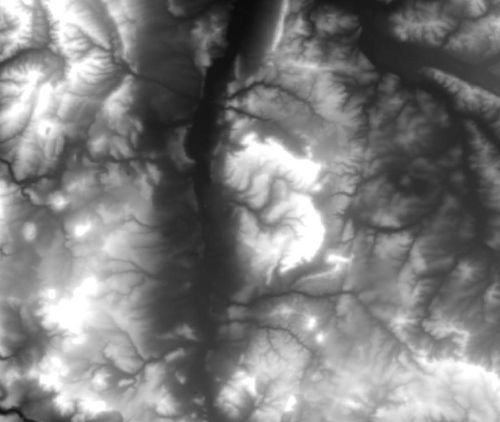
Digital elevation model
- DEM stands for Digital elevation model. It can be represented as a regular grid of points or as a Triangular irregular network of points. DEMs are the basis for digitally produced relief maps.
Digital elevation models are sets of data representing the estimated height of a surface above a certain level, i.e. a Geodetic datum. It may represent the elevation of the bare earth, or include objects as buildings or tree canopies [1].
Contents |
Types of DEMs
There are no official definitions of different subgroups of digital elevation models, but the probably most used terms are Digital surface model (DSM) and Digital terrain model (DTM); the first model may quantify the height of the earth including objects on it's surface, while the latter models the elevation of the mere ground. Still, sometimes both terms are used to describe bare-earth models, leaving the original Digital elevation model term for models including objects above ground level[1].
More specific forms of DEMs sometimes appearing in forestry related publications are Digital Vegetation-height Models (DVM) [2] or Digital Canopy Height Models (DCHM)[3].
Creation of DEMs
Sources
Photogrammetry
- Main article Photogrammetry
Digital elevation models may be obtained by aerial photography and spaceborne instruments such as ASTER, IKONOS or SPOT. The basic principle of photogrammetry is the retrieval of photographs from at least two different positions, which makes the measurement of object heights possible.
Laser Altimetry
- Main article Laser altimetry
Also known as LiDAR, laser altimetry has revolutionized the acquisition of DEM data. LiDAR devices send light pulses to earth and measure the reflection of the ground or objects on it. Time differences between reflected light pulses can be measured, enabling the measurement of object hights.
SAR interferometry
- Main article SAR interferometry
SAR, also referred to as InSAR (Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar), provides an acoustic approach to acquire remote sensing data. Acoustic signals are transmitted and the duration of the reflected signal reaching the sensor is measured. An advantage to the optical systems is it's weather independence, as acoustic noise is able to penetrate clouds [1].
GIS processing
In a GIS, DEMs may be derived from vector data, where each point contains an estimation of the local terrain height. The DEM is then constructed by interpolation of these points.
DEMs in forestry
DEMs may be used in forestry for various research objectives, such as:
- Measuring stand height[2]
- Estimating the mass of above ground carbon [3]
- Hydrological objectives, such as assessing drainage[4] or calculating water flow paths[5]
Digital elevation models are frequently used to estimate other terrain properties, such as slope, aspect and hillshade, or to create viewsheds.
Related articles
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Liu, J. G. & Mason, P. Essential Image Processing and GIS for Remote Sensing. (John Wiley & Sons, 2010).
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Nuske, R. S. & Nieschulze, J. The vegetation height as a tool for stand height determination: An application of automated digital photogrammetry in forestry. Allg. Forst Jagdztg. 175, 13–21 (2004).
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Patenaude, G. et al. Quantifying forest above ground carbon content using LiDAR remote sensing. Remote Sensing of Environment 93, 368–380 (2004).
- ↑ Zhao, Z. et al. Model prediction of soil drainage classes based on digital elevation model parameters and soil attributes from coarse resolution soil maps. Can. J. Soil Sci. 88, 787–799 (2008).
- ↑ Korkalainen, T., Laurén, A., Koivusalo, H. & Kokkonen, T. Impacts of peatland drainage on the properties of typical water flow paths determined from a digital elevation model. Hydrology Research 39, 359 (2008).