Training data selection (SCP)
(→Creating systematic sampling grid) |
(→Creating systematic sampling grid) |
||
| Line 87: | Line 87: | ||
* {{mitem|text=Project --> Project Properties --> CRS}}. Check that the Project spatial reference system is set to '''EPSG:32632'''. | * {{mitem|text=Project --> Project Properties --> CRS}}. Check that the Project spatial reference system is set to '''EPSG:32632'''. | ||
[[File:qgis_goe_syst_sample.png|400px]] | [[File:qgis_goe_syst_sample.png|400px]] | ||
| − | * Click {{button|text= | + | * Click {{button|text=Run}} |
==Stratified random sampling== | ==Stratified random sampling== | ||
Revision as of 18:11, 23 November 2018
Contents |
Defining land use/cover classes
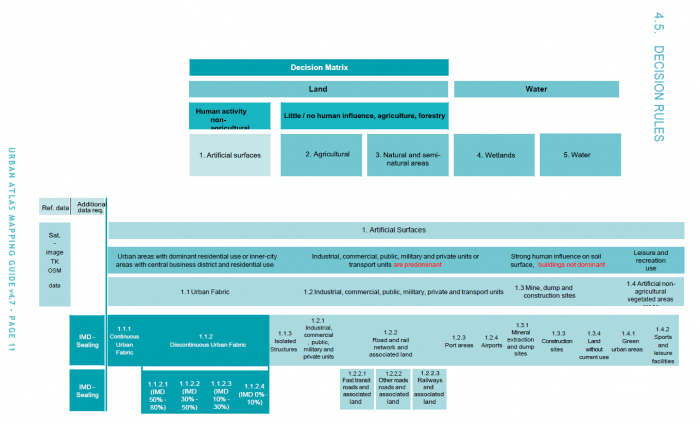
Before starting to map land cover classes using Sentinel-2 satellite images we need clear definitions and a classification scheme. An example for a hierarchical land use and land cover (LUC) classification scheme is the European Urban Atlas. The scheme defines 5 meta classes where the class 1. Artificial surfaces has many sub classes as shown in figure A.
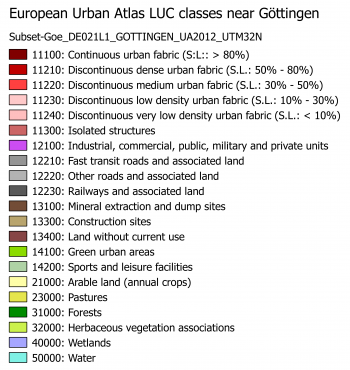
The specification of other meta classes is not as detailed. If we are more interested in forest and open area classes we need to adapt and modify this scheme. On the lowest level not all classes defined in the European Urban Atlas do also appear in the surroundings of Göttingen (figure B). In addition we need to consider the phenolgical development of vegetation at specific acquisiton dates and to specify more classes which can possibly be identified in multispectral feature space of the satellite image. An example of an adapted simplified scheme is shown in the table below.
| MC ID | MC info | C ID | C info | RGB code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Artificial surfaces | 1 | Built-up | 230-0-77 |
| 2 | Agricultural | 2 | Arable land | 255-255-168 |
| 2 | Agricultural | 3 | Bare soil | 253-191-168 |
| 2 | Agricultural | 4 | Pasture | 230-230-77 |
| 3 | Natural and semi-natural areas | 5 | Broad leaved tree cover | 128-255-0 |
| 3 | Natural and semi-natural areas | 6 | Coniferous tree cover | 0-166-0 |
| 5 | Water | 7 | Water | 128-242-230 |
| 0 | Miscellaneous | 8 | No data (cloud) | 255-255-255 |
| 0 | Miscellaneous | 9 | No data (shadow) | 0-0-0 |
| 0 | Miscellaneous | 10 | Unclassified | 0-0-0 |
Creating systematic sampling grid
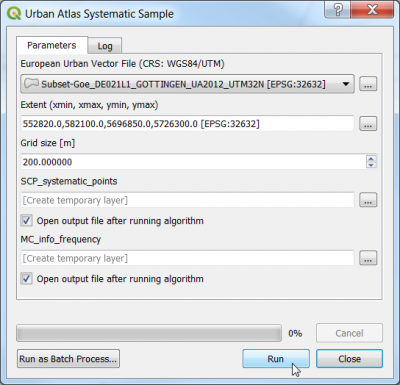
- A processing toolbox model can downloaded from Stud.IP urban_atlas_systematic_sample.model3.
- Open QGIS and go to the Processing Toolbox; if the Toolbox is not opened click Processing --> Toolbox to activate it. Once the Toolbox is opened go to
 Models --> Open existing models and load the previously downloaded model.
Models --> Open existing models and load the previously downloaded model.
- The model should appear in the Models tab. Double click on it to execute.
- Specify an original European Urban Vector File layer for Göttingen: geodata_lab01\vector\DE021L1_GOTTINGEN\Subset-Goe_DE021L1_GOTTINGEN_UA2012_UTM32N.shp or download data from other European cities.
- Project --> Project Properties --> CRS. Check that the Project spatial reference system is set to EPSG:32632.
- Click Run
Stratified random sampling
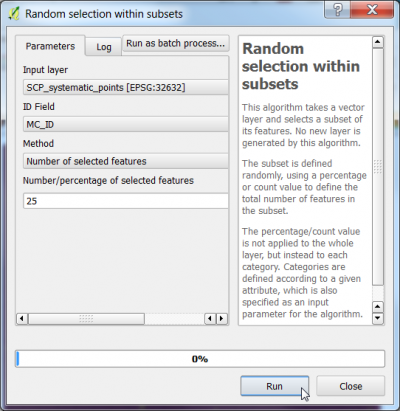
- Vector --> Research Tools --> Random selection within subsets
- The input layer is SCP_systematic_points
- ID Field containing the code for the strata is MC_ID
- Method is equal Number of selected features in each stratum.
- Number of selected features type 25.
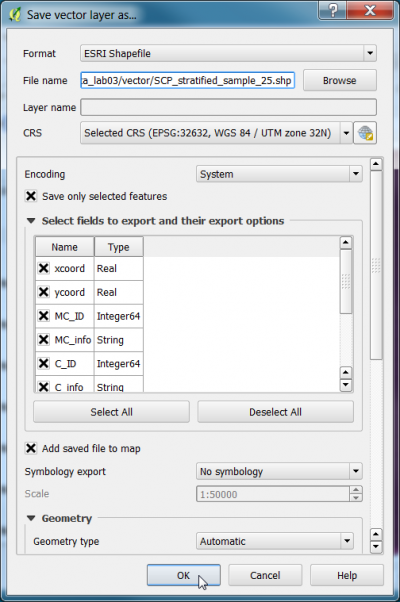
The module selects a subset of the layer SCP_systematic_points. The selected points need to be saved as an ESRI shapefile. Right click on the layer SCP_systematic_points, Save as.... Make sure to check the box: 'Save selected only..as shown below.
Interpretation of selected points
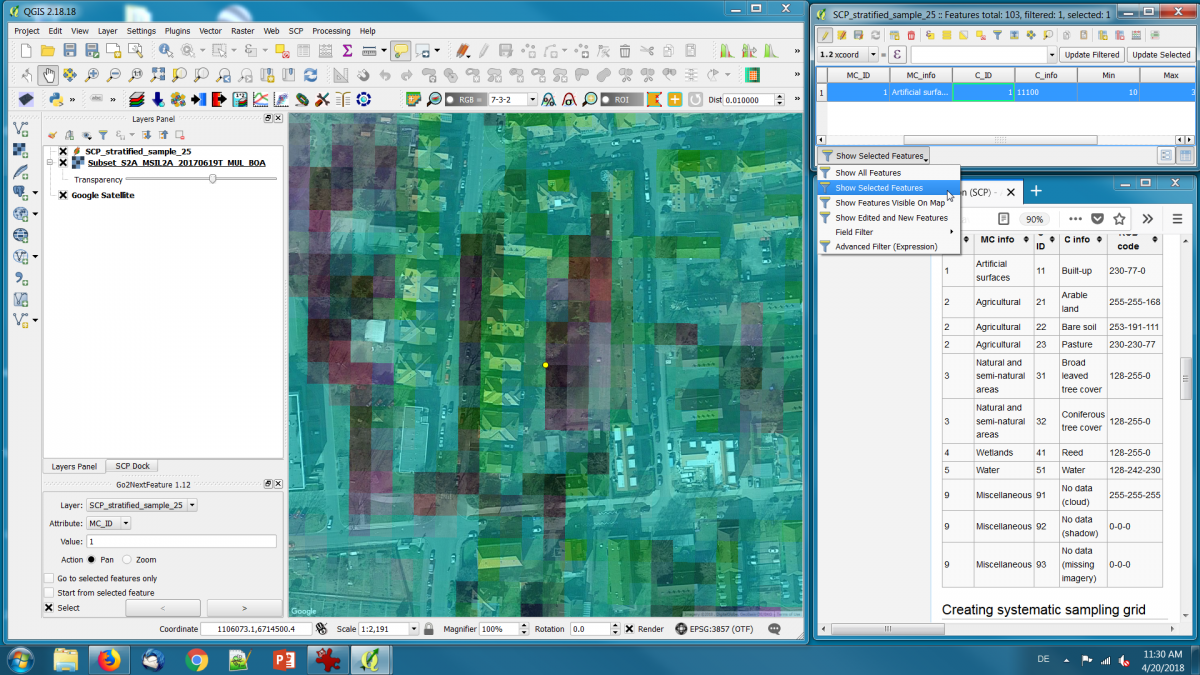
Prepare main QGIS map viewer:
- Install the Openlayers and the Go2nextFeature plugin (if not yet done) Plugins --> Manage and Install Plugins --> Install.
- Load the multiband Sentinel-2 satellite image Subset_S2A_MSIL2A_20170619T_MUL_BOA as surface reflectance (see how to Convert DN to reflectance Land Cover/Use Classification using the Semi-Automatic Classification Plugin for QGIS).
- Create a standard false-color composite (RGB = 7-3-2)(see [Changing Raster Layer Style]]. Set the Layer Properies --> Transparency --> Global Transparency to 50%.
- Load the vector file with stratified sample points SCP_stratified_sample_25.shp.
- Load Google maps as background WMS layer. Web --> OpenLayers Plugin --> Google Maps --> Google Satellite.
- In Layers panel drag the Sentinel-2 image on top of Google Satellite.
- Drag the sample points vector file on top of all other files.
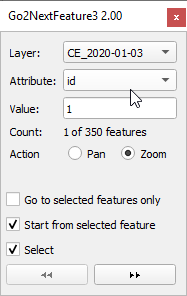
- Activate Plugins -->Go 2 next feature.
- Layer is the sample points.
- The Attribute is MC_ID.
- Click the checkbox Select on.
- In Layers panel right click on the sample point layer and Open Attribute Table.
- On the lower left of the Attribute Table switch from Show All Features to Show Selected Features.
- Start the edit mode of the point layer by clicking the Toggle editing button
 .
.
- Arrange the windows on your Desktop as shown below.