Talk:Land Cover/Use Classification using the Semi-Automatic Classification Plugin for QGIS
From AWF-Wiki
To be updated for QGIS 3
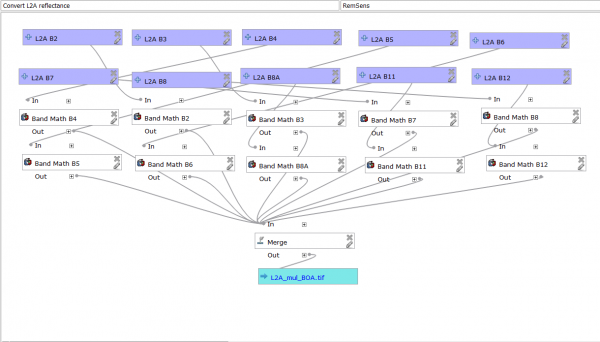
- For these tasks you may also use one processing toolbox model.
- Open the Processing --> Toolbox and Models --> Tools --> Add model from file. Load the previously downloaded model.
- The model should appear in the Models tab.
- Double click to open the model.
- Assign the layers to the right band numbers.
- Click OK
Note: In order to use the batch process in the Raster Calculator you need to first create all of the 9 band split tifs using Translate. Here again you can use the batch processing option.
This batch does not work probably because there seems to be a bug in the processing toolbox raster calculator module: it does not correctly convert the datatype UInt16 to float32:
- Load the multiband raster file Subset_S2A_MSIL2A_20170619T.tif available in the course data. This contains all 13 bands of Sentinel-2 scene.
- Follow Split stack to extract bands 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 11 and 12, using the multiband raster file Subset_S2A_MSIL2A_20170619T.tif as input layer.
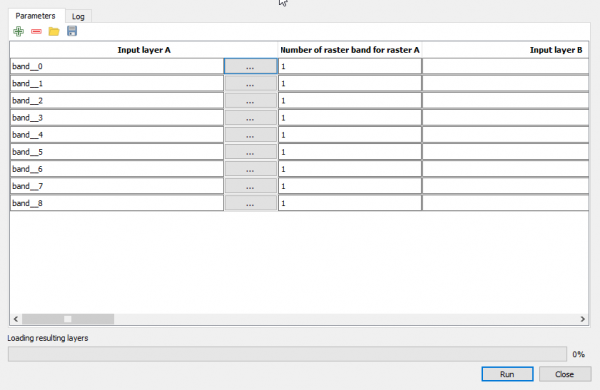
- In the processing toolbar, type Raster calculator into the search field to find the GDAL\OGR --> Raster calculator tool and open it.
- Click the button Run as batch process..., and use Add row
button to add enough processing rows.
- Click the button ... of Input layer A to select the single extracted bands as input layers (i.e. one per row).
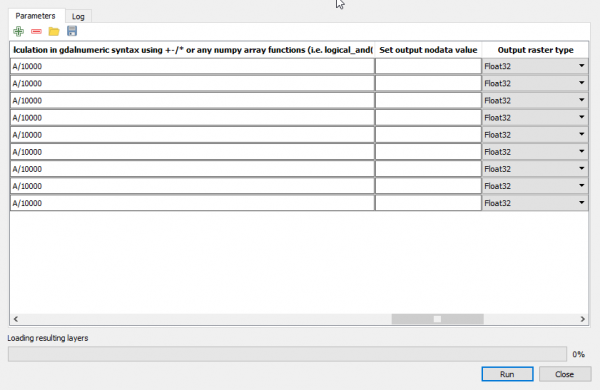
- Enter and repeat the expression A/10000 under Calculation in gdalnumeric syntax using +-/* or any numpy array functions (i.e. logical_and()) and set Output raster type to Float32
- Click the button ... of Calculated to save output file
- Click Run