Land Cover/Use Classification using the Semi-Automatic Classification Plugin for QGIS
From AWF-Wiki
(Difference between revisions)
(→Preparing raster data (Converting DN to reflectance)) |
(→Collection of ROIs and Spectral signatures) |
||
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
==Collection of ROIs and Spectral signatures== | ==Collection of ROIs and Spectral signatures== | ||
| − | # Click on the button {{button|text=Add Vector Layer}} [[Image:QGIS_2.0_addvect.png]] to Load the vector file ''Training_points_refactored.shp'' available in the | + | # Click on the button {{button|text=Add Vector Layer}} [[Image:QGIS_2.0_addvect.png]] to Load the vector file ''Training_points_refactored.shp'' available in the course data and overlay it on the multiband ''Merge''' layer. |
# To display attribute labels for ''Training_points_refactored.shp'', right-click to open {{mitem|text=Properties --> Labels}}. Select '''Show labels for this layer''' and {{button|text=Label with}} '''C_ID'''. | # To display attribute labels for ''Training_points_refactored.shp'', right-click to open {{mitem|text=Properties --> Labels}}. Select '''Show labels for this layer''' and {{button|text=Label with}} '''C_ID'''. | ||
# ROIs can be created by drawing polygons using the button {{button|text=Create a ROI polygon}} [[File:Create_polygon.PNG]] or by an automatic region growing algorithm using the button {{button|text=Activate ROI pointer}} [[File:ROI_pointer.PNG]]. The region growing algorithm can create more homogeneous ROIs (i.e. standard deviation of spectral signature values is low) than manually drawn ones; the manual creation of ROIs can be useful in order to account for the spectral variability of classes. | # ROIs can be created by drawing polygons using the button {{button|text=Create a ROI polygon}} [[File:Create_polygon.PNG]] or by an automatic region growing algorithm using the button {{button|text=Activate ROI pointer}} [[File:ROI_pointer.PNG]]. The region growing algorithm can create more homogeneous ROIs (i.e. standard deviation of spectral signature values is low) than manually drawn ones; the manual creation of ROIs can be useful in order to account for the spectral variability of classes. | ||
Revision as of 14:21, 26 November 2017
Contents |
Working steps
Preparing raster data (Converting DN to reflectance)
- Load the multiband raster file Subset_S2A_MSIL2A_20170619T.tif available in the course data. This contains all 13 bands of Sentinel-2 scene.
- Follow Split stack to extract bands 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 11 and 12, using the multiband raster file Subset_S2A_MSIL2A_20170619T.tif as input layer.
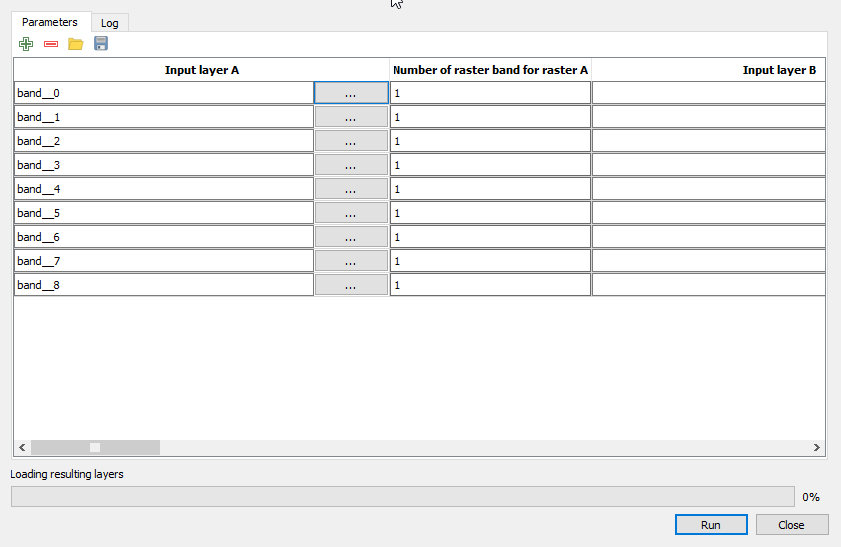
- In the processing toolbar, type Raster calculator into the search field to find the GDAL\OGR --> Raster calculator tool and open it.
- Click the button Run as batch process..., and use Add row
button to add enough processing rows.
- Click the button ... of Input layer A to select the single extracted bands as input layers (i.e. one per row).
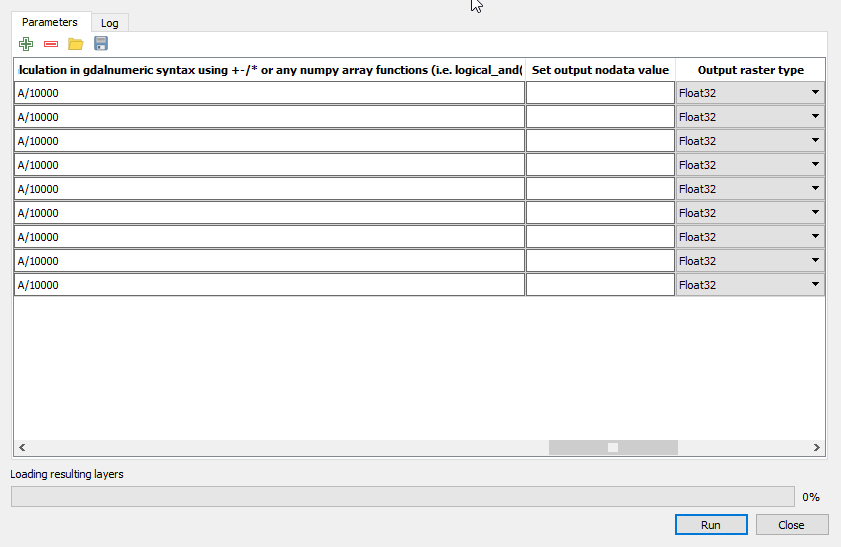
- Enter and repeat the expression A/10000 under Calculation in gdalnumeric syntax using +-/* or any numpy array functions (i.e. logical_and()) and set Output raster type to Float32
- Click the button ... of Calculated to save output file
- Click Run
- Follow Create stack to create a multiband raster file from the converted single bands from step 3 and load into QGIS canvas.
Install and set up SCP plugin
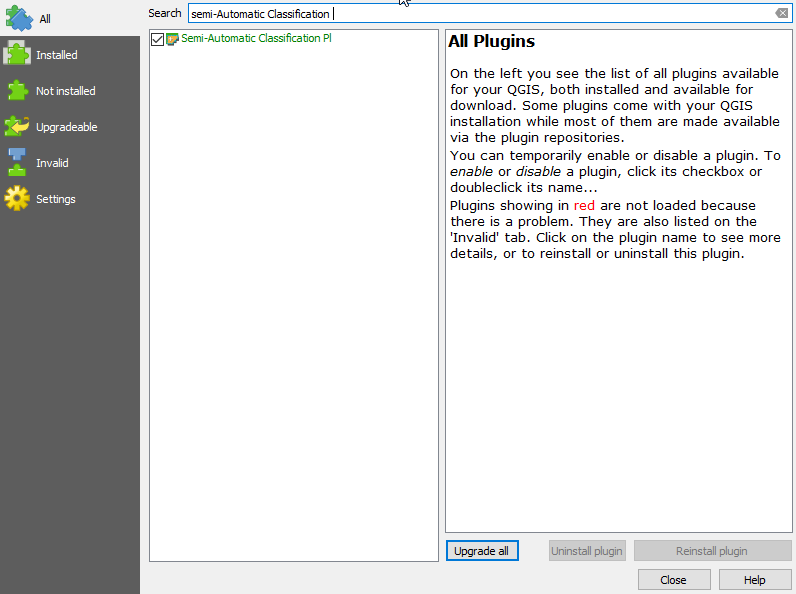
- Click Plugins --> Manage and Install Plugins.
- Type in the search bar semi-Automatic Classification, click on the plugin name and then on Install plugin.
- Right-click on the Plugin Toolbar and make sure the following are checked SCP Dock, SCP Edit Toolbar, SCP Tools and SCP Working Toolbar.
Defining classification inputs in SCP-plugin
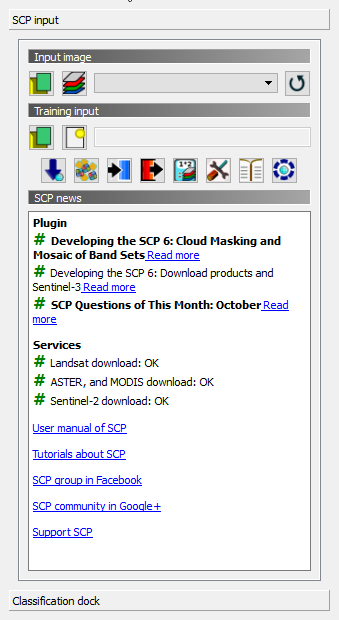
We need to define input image, training input and spectral signature files for SCP.
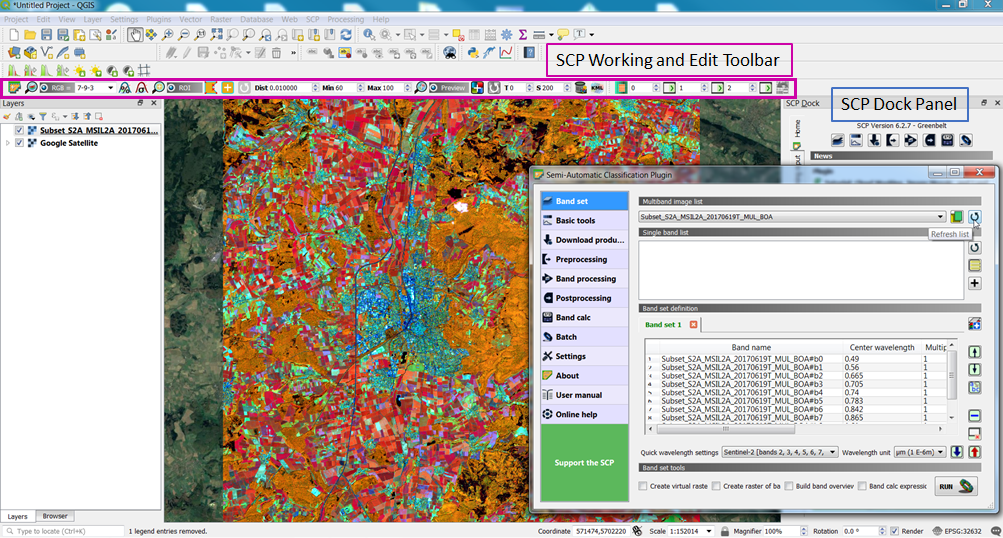
- Open the SCP Dock.
- Click SCP Dock --> SCP input --> Input image, use the button Refresh list
and the drop-down menu-bar to select the multiband Merge file (i.e. from DN to Reflectance conversion) as input image.
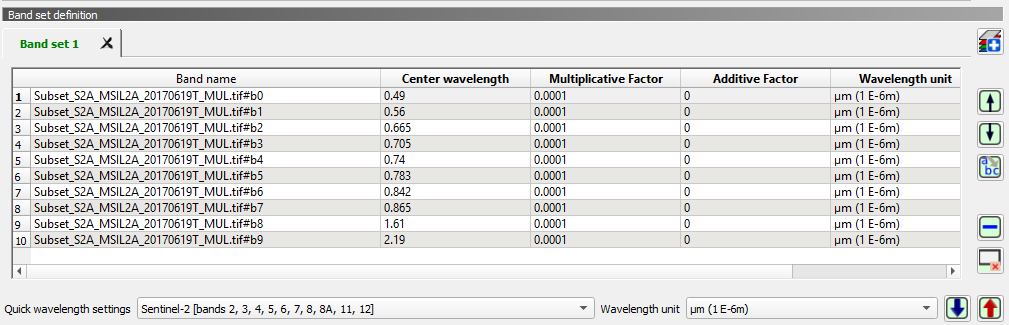
- Click the button Band set
to further define the input image.
- Next, click Quick wavelength settings and select Sentinel-2 from the list in order to automatically set the Center wavelength for each band and the Wavelength unit (NB. required for spectral signature assessment).
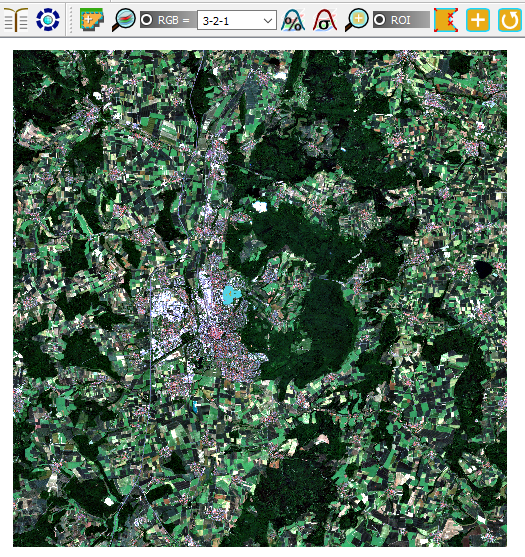
- In the RGB list
of the Working Toolbar, select 3-2-1 to display natural color composite. Also, type in 5-3-2 to display false color composite. While changing the color composite; also use the buttons cumulative_stretch
and std_dev_stretch
for better displaying the Input image (i.e. image stretching).
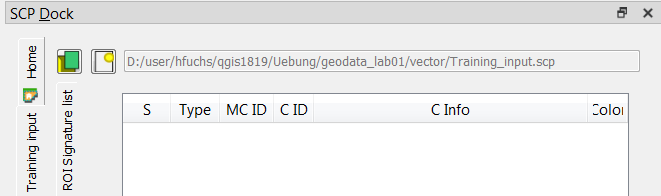
- We need to define training input file in order to collect ROIs and spectral signatures.
- Click SCP Dock --> SCP input --> Training input, use the button Create a new training input
to create the training shapefile, click save.
Collection of ROIs and Spectral signatures
- Click on the button Add Vector Layer
 to Load the vector file Training_points_refactored.shp available in the course data and overlay it on the multiband Merge' layer.
to Load the vector file Training_points_refactored.shp available in the course data and overlay it on the multiband Merge' layer.
- To display attribute labels for Training_points_refactored.shp, right-click to open Properties --> Labels. Select Show labels for this layer and Label with C_ID.
- ROIs can be created by drawing polygons using the button Create a ROI polygon
or by an automatic region growing algorithm using the button Activate ROI pointer
. The region growing algorithm can create more homogeneous ROIs (i.e. standard deviation of spectral signature values is low) than manually drawn ones; the manual creation of ROIs can be useful in order to account for the spectral variability of classes.