Georeferencing of UAV photos
(→Registration of ground control points (GCP)) |
(→Preparation) |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
* Load a vector file with Ground Control Points (GCPs) that were signalized on ground and measured by a differential GNSS reciever. | * Load a vector file with Ground Control Points (GCPs) that were signalized on ground and measured by a differential GNSS reciever. | ||
* Load Google maps as background layer. {{mitem|text=Web --> OpenLayers Plugin --> Google Maps --> Google Satellite}}. The Project Coordinate system switches automatically to ''EPSG:3857, WGS 84 / Pseudo Mercator'' where {{button|text=Enable 'on the fly' CRS transformation}} is checked. \\ | * Load Google maps as background layer. {{mitem|text=Web --> OpenLayers Plugin --> Google Maps --> Google Satellite}}. The Project Coordinate system switches automatically to ''EPSG:3857, WGS 84 / Pseudo Mercator'' where {{button|text=Enable 'on the fly' CRS transformation}} is checked. \\ | ||
| − | In {{tool|text=Layers panel}} drag the GCP vector file on top of ''Google Satellite''. | + | * In {{tool|text=Layers panel}} drag the GCP vector file on top of ''Google Satellite''. |
| + | * Change the color of the point markers: Right click on Layer name in the {{tool|text=Layers panel}} {{mitem|text= Layer Properties--> Style}} | ||
| + | * Show label of the GCP layer. {{mitem|text= Layer Properties--> Label}}. Label with the first column. | ||
== Registration of ground control points (GCP) == | == Registration of ground control points (GCP) == | ||
Revision as of 13:41, 1 November 2017
Contents |
Preparation
- Open Qgis with a new project.
- Install the Openlayers plugin (if not yet done) Plugins --> Manage and Install Plugins --> Install.
- Activate the Georeferencer GDAL plugin (if not yet activated): Plugins --> Manage and Install Plugins --> Installl. Check the box beside the Georeferencer GDAL plugin.
- Prepare main Qgis map viewer:
- Load a vector file with Ground Control Points (GCPs) that were signalized on ground and measured by a differential GNSS reciever.
- Load Google maps as background layer. Web --> OpenLayers Plugin --> Google Maps --> Google Satellite. The Project Coordinate system switches automatically to EPSG:3857, WGS 84 / Pseudo Mercator where Enable 'on the fly' CRS transformation is checked. \\
- In Layers panel drag the GCP vector file on top of Google Satellite.
- Change the color of the point markers: Right click on Layer name in the Layers panel Layer Properties--> Style
- Show label of the GCP layer. Layer Properties--> Label. Label with the first column.
Registration of ground control points (GCP)
- Open Raster –-> Georeferencer -–> Georeferencer.
- Open an mosaic of UAV photos that has no spatial reference system (raw image coordinates).
When the dialog Define spatial reference system appears press ESC.
- Change the band assignment to RGB = 1,2,3. Settings --> Raster Properties --> Style. OK.
- Georeferencer --> Settings --> Configure Georeferencer. Check the box beside 'Show IDS' of the ground control points.
- Add ground control points. First, navigate to a ground control point in the UAV image (e.g. drain cover). Zoom in with the magnifying glass or use the mouse roller.
- Zoom in to a point which you can recognize on both the UAV photo and on Google maps in the main Qgis viewer. In the Layer panel switch topo_utm32_WGS84 on and off. Attention: if the zoom factor is too large Google maps is not displayed in the correct position of the main viewer.
- Click on Add point on toolbar.
A cross shows up. Move the cursor to the first ground control point (e.g. a drain cover or corner of a building). Zoom in and mark the GCP with the cursor and register the position in the image by a left click. A new window Enter map coordinates opens. Click From map canvas. The Georeferencer window will now minimize automatically.
- Click on the same point in Google maps in the main viewer. The coordinates of the main viewer are now transferred directly to the "Enter map cordinates" window. OK.
Zoom to the next control point, activate add point and continue until at least 10 GCPs are registered.
- For changing the position of a point that is already defined activate Move GCP point.
 . Move the point by clicking on it in the Georeferencer viewer.
. Move the point by clicking on it in the Georeferencer viewer.
- For deleting a GCP activate Move GCP point
 and click on it. Alternatively click on a point in the GCP table, right click delete.
and click on it. Alternatively click on a point in the GCP table, right click delete.
- Save the registered GCP points. File --> Save GCP points as .... Save.
Transformation and Resampling
and determine the following settings:
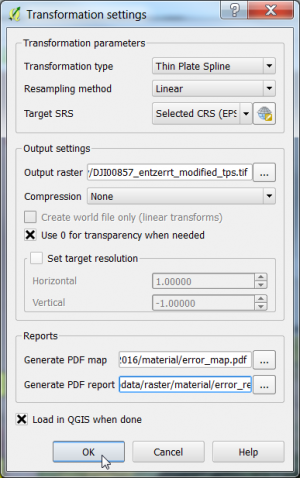
The Target SRS should be the same as the GCP coordinates registered from Google maps: EPSG: 3857, WGS84/ Pseudo Mercator. First, try the transformation type Linear. The horizontal Residuals are now displayed in the last column of the GCP table. In the first column of the table individual points can be switch on or off. Check if the mean error (root mean square error) shown in the grey bar at the bottom of the window can be improved.
- Change the transformation type to Thin Plate Spline. Click on Play
 to create the final georeferenced image file that is loaded into the main Qgis viewer. Compare the results of the two transformation types.
to create the final georeferenced image file that is loaded into the main Qgis viewer. Compare the results of the two transformation types.
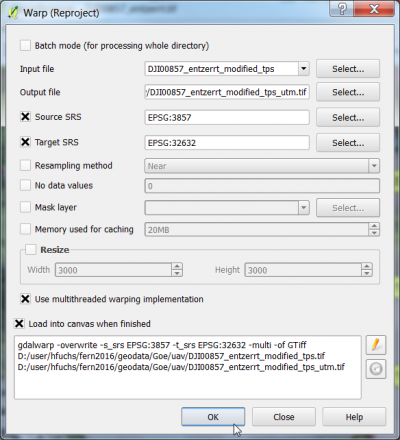
- The SRS EPSG: 3857, WGS84/ Pseudo Mercator does not allow to calculate correct metric distances and areas. Therefore, the georeferenced image needs to be transformed to UTM.
Raster --> Projections --> Warp (Reproject). Determine the following settings:
Quality Check
- Compare the results of the two transformation types Linear and Thin Plate Spline.
- What are the reasons for the large remaining errors?
- How can the Georeferencing result be improved?