Cloud masking
(→Inspect a Sentinel-2 Level-2A Quality index data) |
(→Refining cloud mask) |
||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
[[File:Qgis_cloud_qi_pseudo.png|400px]] [[File:Qgis_cloud_qi_opacity.png|300px]] | [[File:Qgis_cloud_qi_pseudo.png|400px]] [[File:Qgis_cloud_qi_opacity.png|300px]] | ||
| − | = | + | = Convert quality indicator band to a binary cloud mask = |
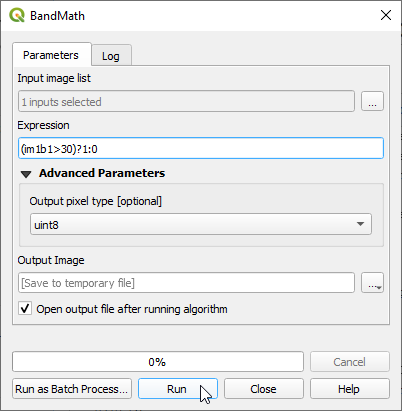
* Create a binary cloud mask (bitmask) where clouds = 1 and non-clouds = 0. Use the Processing tool {{mitem|text= OTB --> Miscellaneous --> Band Math}}. Tick the single band QI layer in the '''Input Image list''' list. You may write a conditional ''ifelse expression'' using lazy operators. Type into the '''Expression''' field: {{typed|text=(im1b1>30)?1:0}} If pixel values of band 1 of multiband image 1 are larger than 30 then replace with 1 otherwise replace with 0. The output pixel type is '''uint16'''. | * Create a binary cloud mask (bitmask) where clouds = 1 and non-clouds = 0. Use the Processing tool {{mitem|text= OTB --> Miscellaneous --> Band Math}}. Tick the single band QI layer in the '''Input Image list''' list. You may write a conditional ''ifelse expression'' using lazy operators. Type into the '''Expression''' field: {{typed|text=(im1b1>30)?1:0}} If pixel values of band 1 of multiband image 1 are larger than 30 then replace with 1 otherwise replace with 0. The output pixel type is '''uint16'''. | ||
[[File:Qgis_cloud_bandmath.png|500px]]] | [[File:Qgis_cloud_bandmath.png|500px]]] | ||
Revision as of 15:03, 10 November 2020
Contents |
Inspect Sentinel-2 quality index data
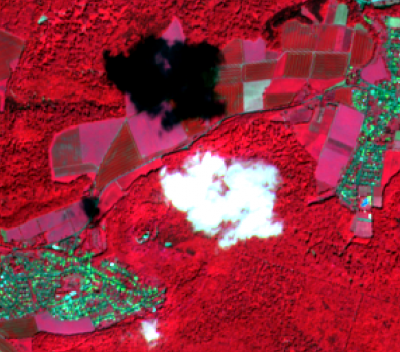
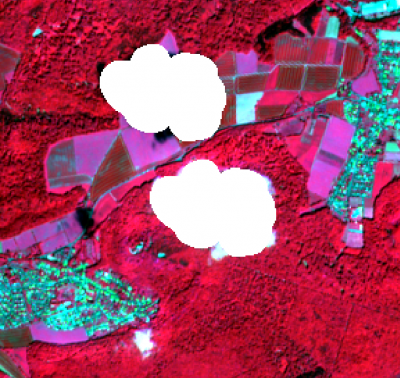
The exclusion of clouds and cloud shadow is an important processing step which is usually done in an early pre-processing stage. The Sentinel-2 products are annotated with Quality Indicators (QI_DATA).
If you use a Sentinel-2 Level 1C product, you'll find a rough dense cloud and cirrus mask (GML vector format) in the folder QI_DATA with the file name MSK_CLOUDS_B00.gml. The vector attribute column masktype distinguishes two classes: OPAQUE (dense clouds) and CIRRUS.
In case of a Sentinel-2 Level 2A product you may find a file in the folder QI_DATA with the extension _CLD_20m.jp2 (data type: 8bit unsigned integer, spatial resolution 20m) which might be used for masking clouds. Data range is from 0 for high confidence clear sky to 100 for high confidence cloudy (for more details see L2A Product Definition Document).
- Load a multiband Sentinel-2 satellite image (Level 2-A product) Changing Raster Layer Style to display a true color (RGB = B4,B3,B2) and a standard false color composite (RGB = B8,B4,B3)
- Zoom in to a cloudy part of the image and compare the extent of cloud and cloud shadow in both composites. Which composite is better for displaying clouds?
- Overlay the QI Cloud band on top of the color composites. Use the Identify Feature Tool for requesting pixel values of the QI band file inside a cloud. Which values represent clouds?
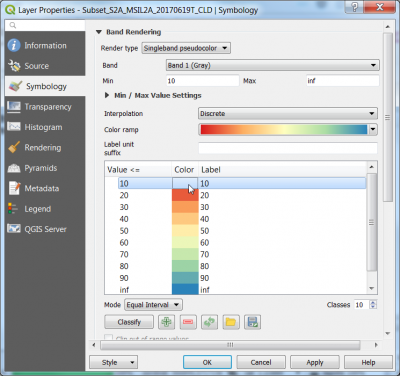
- Change Render type Singelband pseudocolor
- Interpolation is discrete.
- Choose Color ramp spectral
- Mode is equal with
- Interval Classes is 10 as shown in the screenshot.
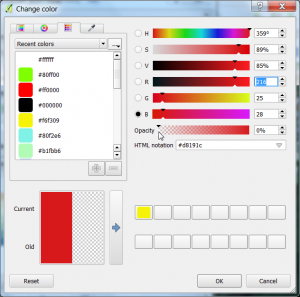
- Double click on a color field of some classes {{mitem|text=Layer --> Properties --> Style) to open the change color window. Change the opacity from 100% to 0%. Find the threshold for clouds.
Convert quality indicator band to a binary cloud mask
- Create a binary cloud mask (bitmask) where clouds = 1 and non-clouds = 0. Use the Processing tool OTB --> Miscellaneous --> Band Math. Tick the single band QI layer in the Input Image list list. You may write a conditional ifelse expression using lazy operators. Type into the Expression field: (im1b1>30)?1:0 If pixel values of band 1 of multiband image 1 are larger than 30 then replace with 1 otherwise replace with 0. The output pixel type is uint16.
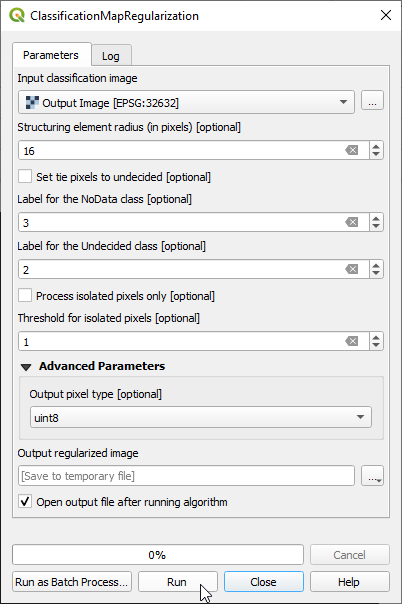
- Apply a circular majority filter with a radius of 16 pixels. Open the Processing tool OTB --> Learning --> ClassificationMapRegularization. The input classifcation image is the Output Image of the band math operation step. Structering element radius is 16 pixels. Adjust Label for NoDat and undecided class. Specify a file name for the Output regularized image. Output pixel type is uint16.
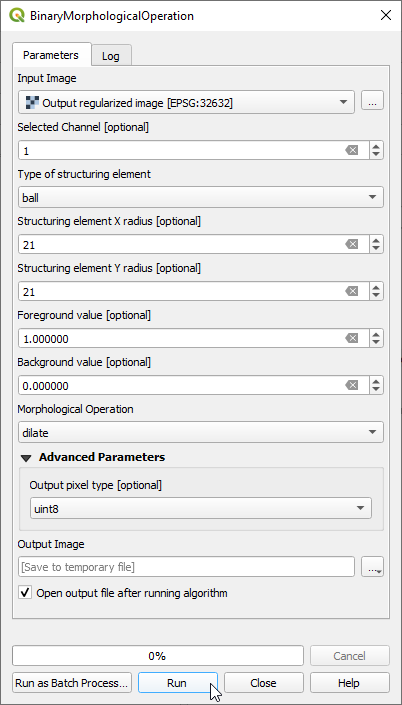
- Open the Processing tool OTB --> Feature Extraction --> BinaryMorphologicalOperation (dilate). Choose the Regularized image as input image. The structuring element type is ball with a radius of 21 pixelsOoutput pixel type is uint16
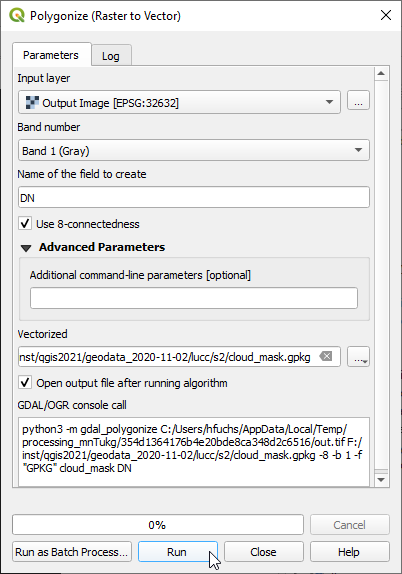
- Convert the Feature Output Imge from raster to vector format. Raster --> Conversion --> Polygonize. Select an output file name for vector polygons.
- Change the display of the output vector polygon layer Layer properties --> Style --> Single Symbol --> Simple Fill --> Fill Style from Solid to No Brush. Change the Outline color to bright green and increase the Outline width. As background layer use a False Color Composite of the Sentinel-2 image.
- Toggle editing
 of the resulting vector polygon layer. Activate Select polygons by dragging a box or by single click
of the resulting vector polygon layer. Activate Select polygons by dragging a box or by single click  , select all polygons with attribute DN = 0 or which are misclassified as clouds and delete them by pressing Del on your keyboard. Save your edits
, select all polygons with attribute DN = 0 or which are misclassified as clouds and delete them by pressing Del on your keyboard. Save your edits  .
.
Creating cloud shadow mask
- Prepare a False color composite of the Sentinel-2 image as background layer in the canvas.
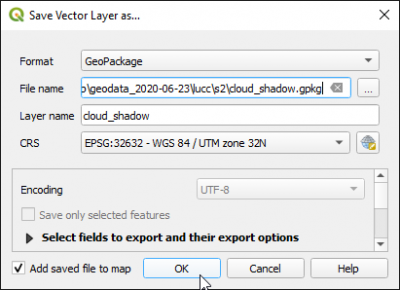
- Right click on the edited polygon layer in the TOC. Choose Export --> Save features as.... Fill the form as shown below.
- Mark the new created polygon layer in the TOC and toggle editing
 of the vector file. Select all polygons using
of the vector file. Select all polygons using  or press Ctrl + A. Activate Edit --> Move feature(s)
or press Ctrl + A. Activate Edit --> Move feature(s)  . Left click on the canvas and move the cloud polygons that shadows on the background false color composite are completely covered. Save your edits
. Left click on the canvas and move the cloud polygons that shadows on the background false color composite are completely covered. Save your edits  and stop editing
and stop editing  .
.
- Select polygons
 outside the image extent of the false color composite and delete them by pressing Del on your keyboard. Save your edits and stop editing
outside the image extent of the false color composite and delete them by pressing Del on your keyboard. Save your edits and stop editing  .
.
Applying cloud and cloud shadow mask
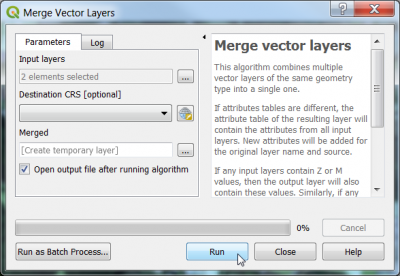
- Vector --> Data management tools --> Merge vector layers. as Layer to merge select the cloud and cloud_shadow polygon layers. Run.
- Create a polygon with the extent of the Sentinel-2 image: Create image extent polygon.
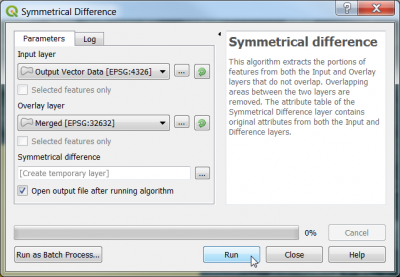
- Vector --> Geoprocessing Tools --> Symmetrical difference. Input layers are the image extent and the merged cloud and cloud_shadow polygons.
- Apply the output vector layer Cleaned as mask to the multiband Sentinel-2 image file. Raster --> Extraction --> Clip Raster by Mask Layer.
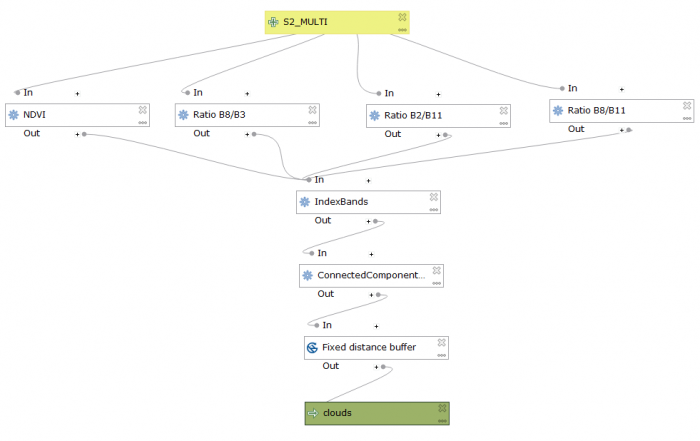
Graphical Processing Tool Model
You can use a prepared graphical processing toolbox model. Download the file from Stud.IP:S2cloudDetection.model3.
- Open QGIS and go to the Processing Toolbox; if the Toolbox is not opened click Processing --> Toolbox to activate it. Once the Toolbox is opened go to
 Models --> Open existing models and load the previously downloaded model.
Models --> Open existing models and load the previously downloaded model.
- The model should appear in the Models tab. Double click on it to execute.
- A window showing the different input and outputs should appear, just as if you were using any other geo-algorithm of the Processing Toolbox.
- You will just need to provide a multispectral Sentinel-2 image file with 10 ordered bands (B2, B3, B4, B5, B6, B7, B8, B8A, B11, B12).