Changing Raster Layer Style
From AWF-Wiki
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
==Render Type: Singleband gray== | ==Render Type: Singleband gray== | ||
==Render Type: Singleband pseudocolor== | ==Render Type: Singleband pseudocolor== | ||
| + | :'' '''Pseudocolor''' is not to be mistaken for [[Color composites|'''false color''']], the latter one being a composite of three bands.'' See also: [[Wikipedia:Pseudocolor#Pseudo-color|Pseudocolor in Wikipedia]] | ||
| + | |||
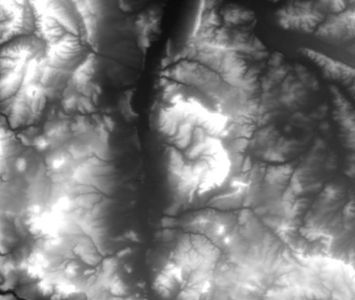
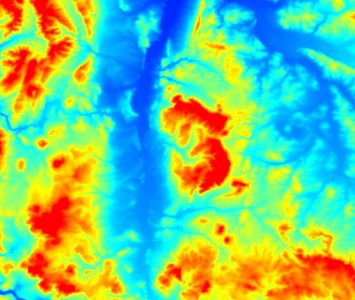
| + | Pseudocolor is a way to display a raster map in which the color scale is derived from a single [[grayscale]] band. In [[Quantum GIS|QGIS]] it can be found in the [[raster layer properties]]. | ||
| + | It can be a good alternative to grayscale if it comes to display metric data like elevation or temperature. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <gallery widths=400px heights=300px> | ||
| + | File:Dem_grey.jpg|A DEM (digital elevation model) displayed in grayscale. | ||
| + | File:Dem_pseudo.jpg|The same DEM displayed in pseudocolor. | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
==Set Transperancy== | ==Set Transperancy== | ||
[[category: Changing Raster Layer Symbology]] | [[category: Changing Raster Layer Symbology]] | ||
Revision as of 15:39, 16 September 2014
The raster layer propertiers differ from the vector layer properties, due to the significant differences of the data. You can open this dialog by double-clicking a raster layer in the TOC or right-clicking on the layer in the TOC and choosing Properties.
Contents |
Render Type: Multiband color
- True color (RGB=3,2,1) simulates the natural color.
- Standard false color (RGB=4,3,2) makes healthy vegetation generally appear red.
- False color (RGB=5,4,3 or 4,5,3) tends to distinguish different landcover material.
- In the Layer stack pulldown-menu, select Yes.
- Click the bottom ... button to select directory and file name to save the result. You can skip this step if you only want to save the result temporarily.
- Check the box Open output file after running algorithm (if not checked per default) and click Run. The resulting map should be added to the TOC automatically after the algorithm has finished, under the name Output layer.
- If necessary, you can rearrange the bands by opening the layer properties and selecting the Style tab. Adjust the bands as you see fit and confirm with Apply or OK (figure B).
- For some color composites, (e.g. true color composites), the image may be enhanced by selecting Stretch to MinMax from the Contrast enhancement menu and selecting the Mean +/- standard deviation x radio button. After adjusting the standard deviation factor (a value between 1 and 2 should do), click Load and confirm with Apply or OK.
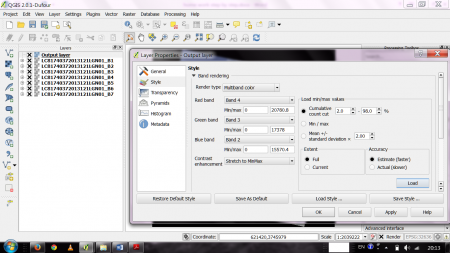
Figure B: The properties dialogue for a multiband raster layer in QGIS 2.0
Render Type: Singleband gray
Render Type: Singleband pseudocolor
- Pseudocolor is not to be mistaken for false color, the latter one being a composite of three bands. See also: Pseudocolor in Wikipedia
Pseudocolor is a way to display a raster map in which the color scale is derived from a single grayscale band. In QGIS it can be found in the raster layer properties. It can be a good alternative to grayscale if it comes to display metric data like elevation or temperature.