Changing Raster Layer Style
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Display of raster data in the map canvas can be enhanced using linear histogram stretching. | Display of raster data in the map canvas can be enhanced using linear histogram stretching. | ||
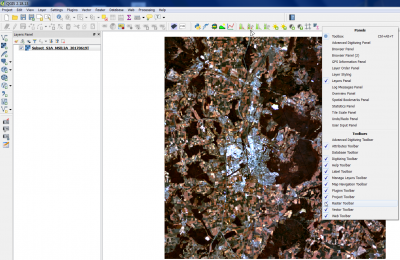
| − | Useful ''Raster tools'' are not activated by default. Right click on the main QGIS menu and activate the checkbox as seen on the screenshot. | + | Useful ''Raster tools'' are not activated by default. Right click on the main QGIS menu and activate the checkbox as seen on the screenshot. A neww Raster Toolbar is now available on the main menu. |
| + | [[File:Qgis_Activate_Raster_Toolbar.png|400px]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Render type: multiband file== | ||
| + | # Click the {{button|text=Add raster layer}} [[Image:QGIS_2.0_addrast.png|20px]] and select the file ''C:/OSGeo4W64/geodata/raster/s2/Subset_S2A_MSIL2A_20170619T.tif''. | ||
| + | # After clicking {{button|text=Open}}, the raster layer appears on the QGIS canvas. | ||
| + | # Right click the layer name in the Layer Panel and select {{mitem|text=Properties --> Style}}. | ||
| + | # Change the assignment of bands of the multiband color. | ||
| + | #True Color composite. | ||
| + | #*Red band: Band 04 | ||
| + | #*Green band: Band 03 | ||
| + | #*Blue Band: Band 02 | ||
| + | In case of our Sentinel-2 example file this is typical True Color composite. You need to be sure about the rank and assignment of spectral bands which depends on the sensor type. | ||
| + | # Standard false color | ||
| + | #*Red band: Band 08 | ||
| + | #*Green band: Band 03 | ||
| + | #*Blue Band: Band 02 | ||
| + | # False color | ||
| + | #*Red band: Band 11 | ||
| + | #*Green band: Band 08 | ||
| + | #*Blue Band: Band 03 | ||
| − | + | You are free to try other false color composites. Find the best Color composite to distingiush forests, urban areas and agriculture. | |
| − | + | # The color composites may be enhanced by selecting {{button|text=Stretch to MinMax}} from the {{button|text=Contrast enhancement}} menu. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | # | + | |
and selecting the {{button|text=Mean +/- standard deviation x}} radio button. After adjusting the standard deviation factor (a value between 1 and 2), click {{button|text=Load}} and confirm with {{button|text=Apply}} or {{button|text=OK}}. | and selecting the {{button|text=Mean +/- standard deviation x}} radio button. After adjusting the standard deviation factor (a value between 1 and 2), click {{button|text=Load}} and confirm with {{button|text=Apply}} or {{button|text=OK}}. | ||
==Render Type: Singleband gray== | ==Render Type: Singleband gray== | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Revision as of 23:17, 22 October 2017
Display of raster data in the map canvas can be enhanced using linear histogram stretching.
Useful Raster tools are not activated by default. Right click on the main QGIS menu and activate the checkbox as seen on the screenshot. A neww Raster Toolbar is now available on the main menu.
 .
.
Contents |
Render type: multiband file
- Click the Add raster layer
 and select the file C:/OSGeo4W64/geodata/raster/s2/Subset_S2A_MSIL2A_20170619T.tif.
and select the file C:/OSGeo4W64/geodata/raster/s2/Subset_S2A_MSIL2A_20170619T.tif.
- After clicking Open, the raster layer appears on the QGIS canvas.
- Right click the layer name in the Layer Panel and select Properties --> Style.
- Change the assignment of bands of the multiband color.
- True Color composite.
- Red band: Band 04
- Green band: Band 03
- Blue Band: Band 02
In case of our Sentinel-2 example file this is typical True Color composite. You need to be sure about the rank and assignment of spectral bands which depends on the sensor type.
- Standard false color
- Red band: Band 08
- Green band: Band 03
- Blue Band: Band 02
- False color
- Red band: Band 11
- Green band: Band 08
- Blue Band: Band 03
You are free to try other false color composites. Find the best Color composite to distingiush forests, urban areas and agriculture.
- The color composites may be enhanced by selecting Stretch to MinMax from the Contrast enhancement menu.
and selecting the Mean +/- standard deviation x radio button. After adjusting the standard deviation factor (a value between 1 and 2), click Load and confirm with Apply or OK.
Render Type: Singleband gray
Render Type: Singleband pseudocolor
- Pseudocolor is not to be mistaken for false color, the latter one being a composite of three bands. See also: Pseudocolor in Wikipedia
Pseudocolor is a way to display a raster map in which the color scale is derived from a single grayscale band. It can be a good alternative to grayscale if it comes to display metric data like elevation or temperature.
To change map color and symbology, again select the layer in the TOC with a right click and select Properties --> Style. From the pulldown menu Render type, select Singleband pseudocolor. A different menu will come up, where you may select the style of the color map in the section Generate new color map. Click classify and confirm with Apply or OK. The map should now appear in the selected style (figure C).