Change detection
(→Multi-temporal color composite) |
(→Principal component analysis) |
||
| Line 84: | Line 84: | ||
=== Principal component analysis === | === Principal component analysis === | ||
| − | + | Perform a [[Principal component analysis]] on stacked multitemporal NDVI images. | |
| − | + | Enter 3 as number of components and visualize the as color comoposite. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
[[category:QGIS Tutorial]] | [[category:QGIS Tutorial]] | ||
Revision as of 22:20, 14 January 2018
Contents |
Prerequisites of spatio-temporal image analysis
Correct the pixel intensities as much as possible for uninteresting differences:
- Sensor calibration
- Exact spatial co-registration of images (especially pixel-by-pixel comparision)
- Cloud and cloud shadow masking
- Haze reduction
- Atmospheric correction
- Topographic illumination correction (mountains)
- Clear definitions and classification scheme
Visualization of multi-temporal images
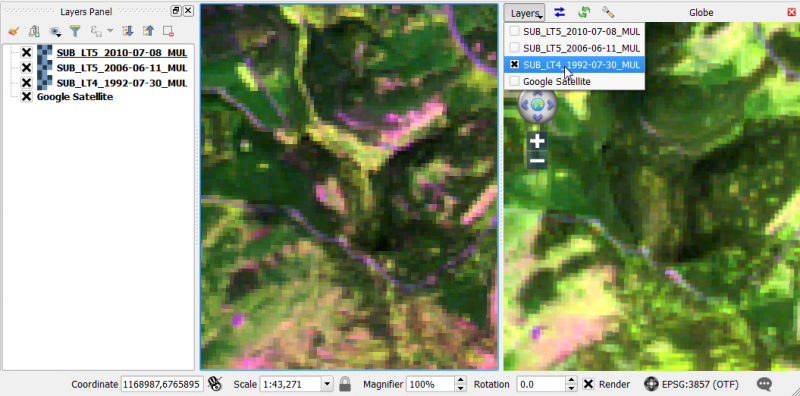
- Add subsets of 3 Landsat TM multispectral scenes of 1992 (SUB_LT4_1992-07-30_MUL.tif), 2006 (SUB_LT5_2006-06-11_MUL.tif)and 2010 (SUB_LT5_2010-07-08_MUL.tif) into the QGIS TOC.
- Create color composites RGB=(B5 SWIR-1),(B4 NIR), (B3 Red) following Changing Raster Layer Style of a multiband file.
- Select Web --> OpenLayers plugin --> Google Maps --> Google Satellite. If the Plugin doesn't exist you'll first have to install the Openlayers plugin using Plugins --> Manage and install plugins. A new Layer Google Maps is loaded. The project CRS is automatically set to WGS84/Pseudo Mercator (EPSG:3857). Drag and drop the Layer to the bottom of the TOC.
Globe plugin
- The Globe plugin is already installed. It just needs to be activated.
Plugins --> Manage and Install Plugins --> Installed. Click the checkbox or doubleclick the name Globe to activate the plugin.
- Plugins --> Globe --> Launch Globe. The Globe windows opens side by side to the map canvas.
- In the Globe viewer click on Globe settings
 . Switch off the atmosphere rendering by unchecking the box Sky. OK.
. Switch off the atmosphere rendering by unchecking the box Sky. OK.
- Adjust the size of the Globe viewer to the same size as the map canvas.
- In the map canvas zoom in to a region of interest. Adjust the local histogram stretch for all layers in the TOC clicking
 (Raster Tools).
(Raster Tools).
- In the Globe Viewer click on Layer Layer and check the layers that you would like to see oon top of the Globe Viewer. Attention uncheck the layer Google Satellite in the Globe Viewer: otherwise QGIS crashes!
- Click first on Reload layer
 and then Synchronize extent
and then Synchronize extent  . The extents of the canvas and the Globe viewer are synchronized as shown below.
. The extents of the canvas and the Globe viewer are synchronized as shown below.
MapSwipe Tool plugin
This plugin is a map tool for swipe active layer, for example, you can see the difference with others layers below. The active layer, or group, will appear above all others.
- Select Plugins --> MapSwipe Tool or click
 . If the Plugin doesn't exist you'll first have to install it. Check Plugins --> Mange and Install plugins.. --> Settings Show also experimental plugins.
. If the Plugin doesn't exist you'll first have to install it. Check Plugins --> Mange and Install plugins.. --> Settings Show also experimental plugins.
- Mark a layer below the top layer in the TOC and hold left click to blend to and compare two layers.
- Do not mark Google Satellite as active layer, otherwise QGIS crashes!
Temporal/Spectral Profile plugin
Change detection techniques
Bitemporal
Post-classification Comparison
This is an indirect change detection method: First two co-registered satellite images are independently classified to yield thematic maps. Then, discrete class labels of two thematic raster layers are compared to determine changes using cross-tabulation in which all transitions are presented. Use the Semi Automatic Classification plugin: Postprocessing --> Land cover change
Raster algebra: Difference
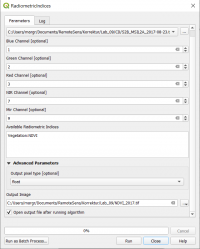
- In the search engine of the Processing Toolbox, type Radiometric and select Radiometric Indices under Feature Extraction of the Orfeo Toolbox.
- Select the Landsat TM SUB_LT4_1992-07-30_MUL.tif file as input layer.
- Assign the spectral bands to the right band number as shown below.
- Choose ndvi from the Available Radiometric Indices drop-down list to calculate the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI).
- Enter name and path for an output file.
- Click on Run.
- Calculate also the NDVI of the Landsat images SUB_LT5_2006-06-11_MUL.tif and SUB_LT5_2010-07-08_MUL.tif.
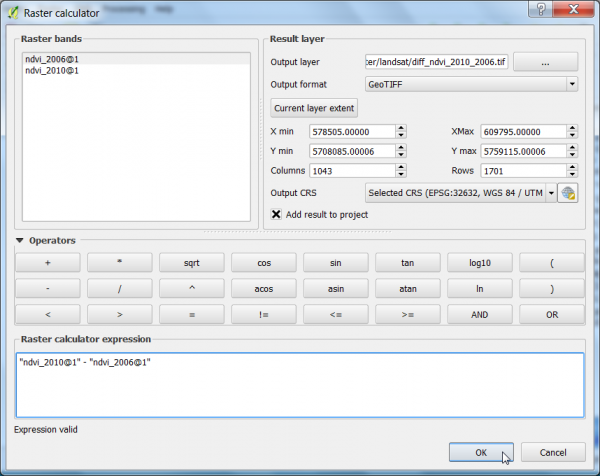
- Calculate the difference between the NDVI 2010 and NDVI 2006 using the Raster Calculator.
- Click Raster --> Raster calculator.
- A difference NDVI is calaculated by the expression as shown below.
- Define path and file name of the output layer. OK.
- Mark the difference NDVI image right click Properties --> Metadata
 . In the "properties" window scroll down and report mean STATISTICS_MEAN and standdard deviation STATISTICS_STDDEV.
. In the "properties" window scroll down and report mean STATISTICS_MEAN and standdard deviation STATISTICS_STDDEV.
- Find threshold values for forest change areas: Calculate threshold1 = mean - stddev and
threshold2 = mean + stdev.
- Layer Properties --> Histogram to plot the difference histogram.
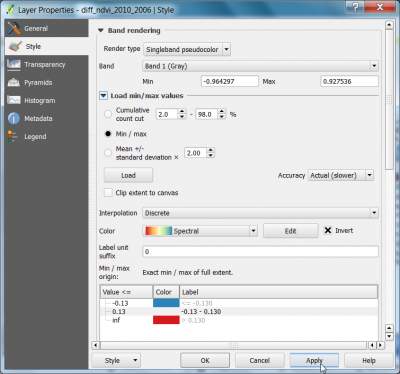
- Layer Properties --> Style. Change Render type to Singleband Pseudocolor
- Load min/max values: Activate the radio button Min / max.
- Choose Accuracy: Actual(Slower) and click Load.
- Choose Interpolation: Discrete.
- Select a color table. Color: Spectral. Check Invert.
- Mode: Equal area. Number of Classes: 3.
- Type for Value <= :
first line: -0.13 (threshold1)
second line -0.13 (threshold3)
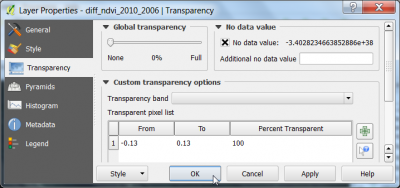
- Layer Properties --> Transparency. Click
 to add a new line in the pixel transparency list. Type values From: -0.13 and To: -0.13. OK. The specified range of the difference raster is now transparent and can be overlaid on top of Google Satellite and the Landsat composites.
to add a new line in the pixel transparency list. Type values From: -0.13 and To: -0.13. OK. The specified range of the difference raster is now transparent and can be overlaid on top of Google Satellite and the Landsat composites.
Raster algebra: Ratio
- Calculate the ratio of raster images 2010 and 2006 with the Raster --> Raster Calculator.
- Choose ndvi_2010@1 from the Raster bands by double clicking on the raster name.
- Choose the division operator from the Operators by clicking on /.
- Choose ndvi_2006@1.tif from the Raster bands by double clicking on the raster name.
- Save the Output layer as ndvi_ratio and press OK.
Multi-temporal
Multi-temporal color composite
- Stack three ndvi raster files from three different dates with Toolbox --> GDAL/OGR --> [GDAL] Miscellaneous --> Merge. See also Create stack.
Principal component analysis
Perform a Principal component analysis on stacked multitemporal NDVI images. Enter 3 as number of components and visualize the as color comoposite.