Object-based supervised classification
From AWF-Wiki
Contents |
Object-based image analysis (OBIA) with QGIS and OTB processing plugin
Segmentation
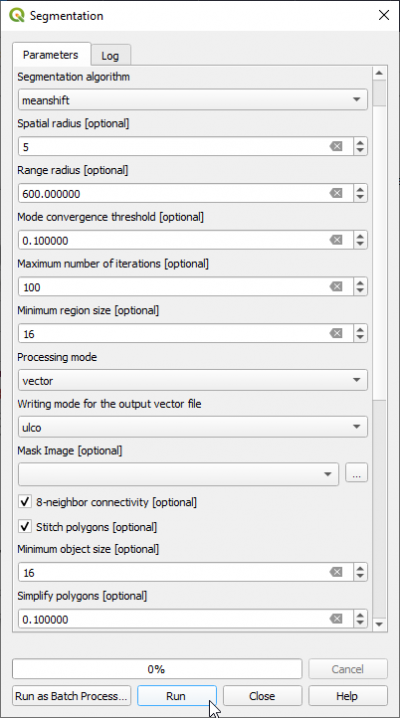
- In the search engine of Processing Toolbox, type segmentation and double click Segmentation.
- Select the input image: Subset_S2A_MSIL2A_20170619T_MUL.tif (data type uint 16bit).
- Set Segmentation algorithm to meanshift
- The Range radius value can be set to 600. The optimal value depends on datatype dynamic range of the input image and requires experimental trials for the specific classifcation objectives.
- Set Minimum Region size (in pixels) to 16.
- Processing mode Vector
- Set the Mask image to blank (top of drop-down list).
- Check 8-neighborhood connectivity on.
- The Minimum object size (in pixels) can be set to 16 depending on minimum mapping size.
- Change Output pixel type to uint32.
- Name the Output vector file e.g. segments_meanshift.gpkg (GeoPackage).
- Click Run.
- Evaluate the segmentation results: Load the output vector file segments_meanshift.gpkg into QGIS on top of the image Subset_S2A_MSIL2A_20170619T_Mul.tif
Mark the vector layer in the Qgis Layers window. Right click Properties --> Symbology --> Simple Fill, Fill Style: No Brush and Stroke color:white.
Feature extraction
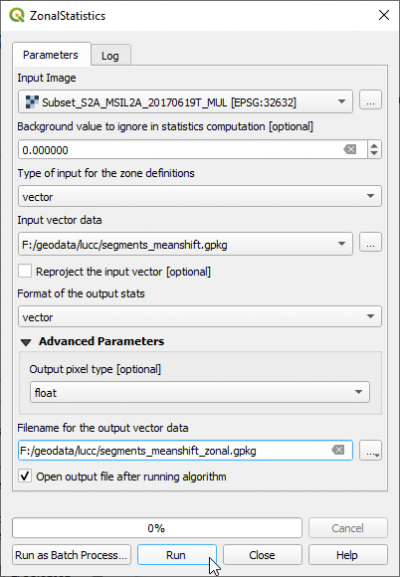
In the search engine of Processing Toolbox, type zonalstats and open ZonalStatistics under Image Manipulation of OTB.
- Select the Input image: Subset_S2A_MSIL2A_20170619T_MUL.tif.
- Background value to ignore: 0
- For the Input vector data do not select a vector file from the file list which are already loaded in the QGIS Viewer. There is currently a bug in QGIS 3.16 which leads to failure because the full pathname is not parsed correctly. Instead, please select a vector file by clicking
 and browse directly to the file containing the result from Segmentation: segment polygons in format GPKG segments_meanshift.gpkg.
and browse directly to the file containing the result from Segmentation: segment polygons in format GPKG segments_meanshift.gpkg.
- File name for the output vector data: segments_meanshift_zonal.gpkg.
- Click Run.
Training phase
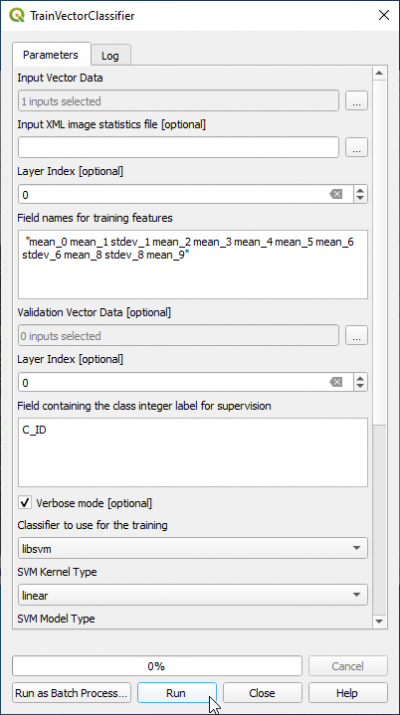
- In the search engine of Processing Toolbox, type Train and double click TrainVectorClassifier.
- In the Input Vector Data List do not select a file from the list which is already loaded in the QGIS Viewer. There is currently a bug in QGIS 3.16 which leads to failure during file import. Instead please select a vector file clicking
 and browse directly to the file containing training area polygons in format GPKG or SHP e.g. lucc_training_obia.gpkg.
and browse directly to the file containing training area polygons in format GPKG or SHP e.g. lucc_training_obia.gpkg.
- Output model filename is svm_obia.model
- In the field Field names for training features copy and paste
"mean_2 stdev_0 mean_9 mean_7 mean_0"
- This is one of many variable sets as a result of a feature selection procedure.
- The name of Field containing the class id for supervision" is C_ID.
- Classifier to use for training: libsvm
- SVM Kernel Type: linear
- SVM Model Type: csvc
- Click Parameters optimizationON.
- Click Run.
 Info
Info
- For more detailed information on the SVM algorithm visit the LibSVM website
Classification phase
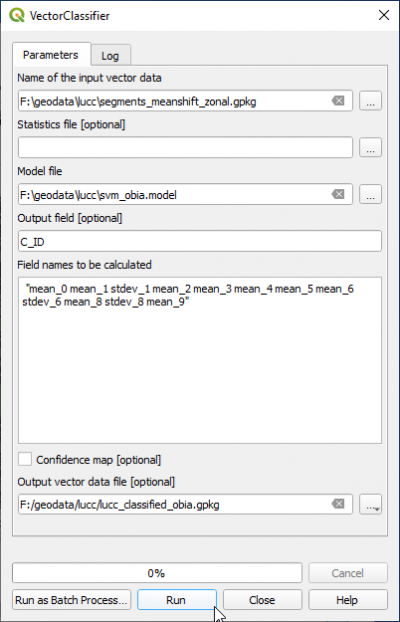
- In the search engine of Processing Toolbox, type Vector and double click VectorClassifier.
- In the Input Vector Data do not select a file from the list which is already loaded in the QGIS Viewer. There is currently a bug in QGIS 3.16 which leads to failure during file import. Instead please select a vector file clicking
 and browse directly to the file containing segments and features for the whole image (result of Feature extaction)training area polygons in format GPKG segments_meanshift_zonal.gpkg.
and browse directly to the file containing segments and features for the whole image (result of Feature extaction)training area polygons in format GPKG segments_meanshift_zonal.gpkg.
- Name of the input model file is svm_obia.model.
- Output field containing the class is C_ID
- Copy and paste into the field Field names to be calculated have to be the same features for prediction as were defined before in the TrainVectorClassifier module:
"mean_2 stdev_0 mean_9 mean_7 mean_0"
- Output vector Data file is lucc_classified_obia.gpkg.
Run.
Load the output vector file manually into QGIS. Layer --> Layer properties --> Symbology > Style --> Load style.... Open the same QGIS style file which is already in use for the training data: lucc_training_obia.qml.