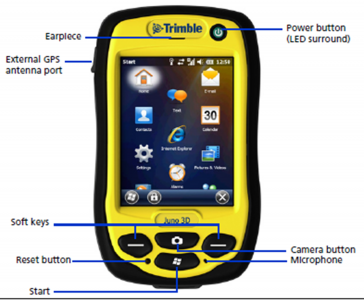
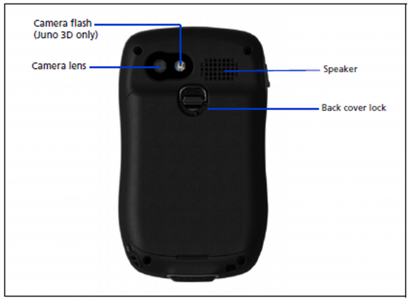
Trimble Juno GPS
From AWF-Wiki
Author of this article: Yanti Sarodja
In this exercise you'll get an introduction on how to handle a the
GPS receiver Trimble Juno 3B by Trimble navigation.
Contents |
Startup and configuration
- Press the power button for a few seconds
- Open the windows menu (by selecting on screen or pushing the windows-button) and select TerraSync --> Professional Edition. You are redirected to the Status menu, with a compass rose displayed in the center of the screen. Wait for a few minutes, until you get a connection to at least three satellites, which are displayed by little symbols on the compass rose.
- Set the coordinate system and other parameters
- To set the coordinate system and other parameters, select the upper of the two pull down menus at the top left corner of the screen (right now, Status should be displayed here). Select Setup. Alternatively, you can select the wrench symbol to enter the setup menu (see figure A).
- Select the Coordinate system menu.
- Set all parameters to the desired configuration:
- For this exercise, you can select Germany under System, UTM Zone 32 as the Zone and WGS 1984 as the Datum. Leave all other configurations as they are.
- Confirm with Done.
To find a specific spatial point:
- Set the target
- Select the upper pull-down menu, which now should display Status. Select Data, and select Existing file from the pulldown menu below.
- Select the device where the data is stored under Location. Some exemplary data is stored under Storage card. Select Tree waypoints from the displayed file list and click Open. Just confirm the dialogue prompting you for the antenna height. A list with wayponints should appear.
- Select the point you want to navigate to (e.g. Tree01).
- Click Options-->Set Nav Target and set the point you selected before.
- Set the background map
- Select the upper pulldown menu and Map.
- Click Layers and check make sure that Background and GNSS trail are checked. Select the Background files... menu and check the file(s) you want to load. (e.g. aerial_utm32_WGS84n) and confirm with Done. The background map should now be displayed (see Figure B).
- To zoom in to your location on the map, select Option --> Auto pan to GNSS position or Auto pan to selection for manual zooming.
- Your position appears as x and the selected target as flag symbols on the map.
- Navigation to the target:
- Select Navigation from the top-left pulldown menu.
- Follow the displayed compass and also check the Distance field at the bottom-left of the screen. Note that you need to move to get the compass working.
- To add an own ground control point (GCP):
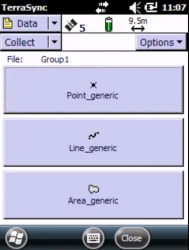
- Standing at the desired point, select Data from the top-left pulldown menu. From the pulldown menu right below, select New and enter the name of the point (e.g. GCP01). Confirm by clicking Create. Also confirm the antenna-height prompt as it is.
- In the next menu, sellec Point generic. You can add a comment to give the point a label (for simplicity, you may just enter the name again).
- Before you're done, the spatial data of the ppoint must be updated. In order to do this, first select Options --> Logging interval and set the interval to 1 second.
- Click the Log button. A counter will appear at the top-right corner of the screen. Wait until it has reached 100 and press Done. Confirm with Yes and your point is saved.
Show the background and shapefile
- Click on the top-left dropdown list / Select Navigation / Select Navigate
- Click on the Nav dropdown list / Select Status
- The Skyplot window appears / Check for the satellite and the accuracy received by the devices
- Click on the top-left dropdown list / Select Map
- A new window appears / Select Background Files
- A Background Files window appears, Use this setting
- Location: Storage Card
- Thick the check box in front of Show data files
- Thick the check box in front of pky_re8b_dd (background map) and 14080701a (road and gcp location)
- Click Done when everything is set
- The background map and the shapefile will appear on the window. Use the dropdown list on the Top-left corner of the window to select, zoom in, zoom out, pan, digitize, or measure
Collecting and saving GCPs
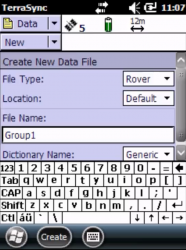
- Click on the top-left dropdown list / Select Data
- A Create New Data File window appears; Use this setting;
- File Type: Rover
- Location: Storage Card (ALWAYS use STORAGE CARD)
- File name: gcp01 / gcp 02/ gcp 03 / … / gcp12
- Dictionary name: Generic
- Click create (at the bottom-center menu)
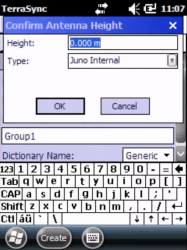
- Confirm Antenna height window appears, click OK (use default setting)
- Another window appears, Select/click on the Point_generic, click Log (on the bottom-right menu)
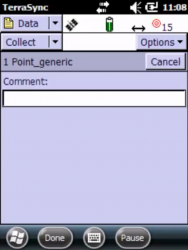
- On the Upper-right menu, a red circle will appear and starts blinking. The blinking represents how many seconds (and measurements) are taken. Wait until at least 120 seconds (2 minutes) (see the arrow on the Right picture)
- While waiting, we can also type a short description of the point in Comment
- Click Done when it finish / Click Yes to save the position / Click Close (on the bottom-right menu) / Click Yes to close the file. Make sure all this procedure has been done to save and close the file completely.
- Take a picture of the GCP location using the device; Press the icon for 2-3 second / The window will change to a picture scene / Press the icon again to make a picture / Press the left icon continue by pressing the right icon to go back to the map window
- Describe the exact location where the GCP is taken on the field form (a clue to find the location in the background image). A drawing would be helpful.
Repeat the procedure to collect and save the next GCP.
ALWAYS create a new file for a new GCP. Make sure that one file is use to collect and save only one GCP to avoid any overwrite points.