Stratified sampling examples
(→Example 1) |
(→Example 1) |
||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
'''Table 1''' Stratum parameters for the stratified example population. | '''Table 1''' Stratum parameters for the stratified example population. | ||
| − | |||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 36: | Line 35: | ||
|2.48 | |2.48 | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | + | </div> | |
Calculation in stratified sampling is best done in tabular format, first per stratum and then combining the per-stratum results to the values / estimations for the entire population. The estimation of the mean is illustrated in Table 2 and results – as expected – in the parametric mean without stratification. Table 3 presents the calculation of the parametric error variance for <math>n=10</math> and the defined allocation of samples to the three strata. | Calculation in stratified sampling is best done in tabular format, first per stratum and then combining the per-stratum results to the values / estimations for the entire population. The estimation of the mean is illustrated in Table 2 and results – as expected – in the parametric mean without stratification. Table 3 presents the calculation of the parametric error variance for <math>n=10</math> and the defined allocation of samples to the three strata. | ||
| Line 42: | Line 41: | ||
'''Table 2''' Calculation of parametric population mean from the parametric strata means. | '''Table 2''' Calculation of parametric population mean from the parametric strata means. | ||
| − | |||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 70: | Line 68: | ||
|'''7.0667''' | |'''7.0667''' | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | + | </div> | |
Revision as of 19:09, 16 December 2010
Example 1
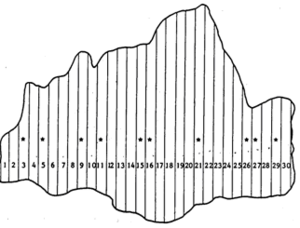
This example shows stratified sampling by the example population from figure 1.
Imagine the example population of \(N=30\) elements be subdivided into three strata as in figure 2. Here, stratification has been done arbitrarily into three strata of size 14, 8 and 8. From this stratified population, we wish to take a sample of \(n=10\), taking \(n_1=4\) from the first stratum and \(n_2=n_3=3\) from the other two strata. The stratum parametric means and variances are given in table 1.
Table 1 Stratum parameters for the stratified example population.
| Stratum | \(N_h\,\) | \(n_h\,\) | \(\mu_h\,\) | \(\sigma_h^2\,\) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 14 | 4 | 6.29 | 3.49 |
| 2 | 8 | 3 | 10.13 | 4.86 |
| 3 | 8 | 3 | 5.38 | 2.48 |
</div>
Calculation in stratified sampling is best done in tabular format, first per stratum and then combining the per-stratum results to the values / estimations for the entire population. The estimation of the mean is illustrated in Table 2 and results – as expected – in the parametric mean without stratification. Table 3 presents the calculation of the parametric error variance for \(n=10\) and the defined allocation of samples to the three strata.
Table 2 Calculation of parametric population mean from the parametric strata means.
| Stratum | Stratum mean | Weight \((W_h)\) | mean*weight |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 6.29 | 0.466667 | 2.9333 |
| 2 | 10.13 | 0.266667 | 2.7000 |
| 3 | 5.38 | 0.266667 | 1.4333 |
| 7.0667 |
</div>
| sorry: |
This section is still under construction! This article was last modified on 12/16/2010. If you have comments please use the Discussion page or contribute to the article! |