Convert vector to raster
From AWF-Wiki
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
# Define path and name for the single band output layer. | # Define path and name for the single band output layer. | ||
# Click on the ‘OK-button’. | # Click on the ‘OK-button’. | ||
| + | # In the processing toolbar, type {{typed|text=Translate}} into the search field to find the {{button|text=GDAL\OGR --> Translate (Convert format)}} tool and open it. | ||
| + | ** Type in the textbox '''Nodata value''': {{typed|text=0}} | ||
| + | ** Unfold the '''Advanced parameters''' and change the output data format to unsigned 16bit integer): {{typed|text=-ot UInt16}} | ||
| + | ** Click the button {{button|text=...}} of '''Converted''' to select path and name of output file. | ||
| + | ** Click {{button|text=Run}}. | ||
[[category:Working with Vector Data]] | [[category:Working with Vector Data]] | ||
Revision as of 00:31, 26 November 2017
- Click the Add raster layer
 and select the file C:/OSGeo4W64/geodata/raster/s2/Subset_S2A_MSIL2A_20170619T.tif.
and select the file C:/OSGeo4W64/geodata/raster/s2/Subset_S2A_MSIL2A_20170619T.tif.
- Click Open, the raster layer appears on the QGIS canvas.
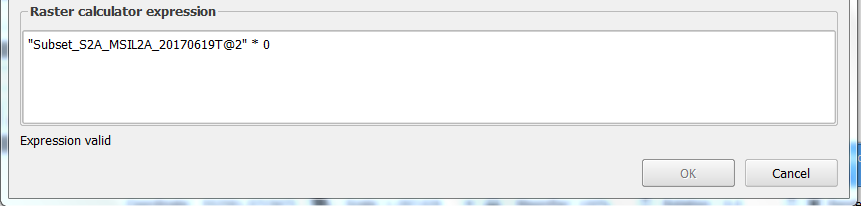
- Open the raster calculator and apply the following formula:
- Define path and name for the single band output layer.
- Click on the ‘OK-button’.
- In the processing toolbar, type Translate into the search field to find the GDAL\OGR --> Translate (Convert format) tool and open it.
- Type in the textbox Nodata value: 0
- Unfold the Advanced parameters and change the output data format to unsigned 16bit integer): -ot UInt16
- Click the button ... of Converted to select path and name of output file.
- Click Run.