Digitizing training and test areas
From AWF-Wiki
(Difference between revisions)
(→Working steps) |
|||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
==Working steps== | ==Working steps== | ||
# Generating sample points | # Generating sample points | ||
| − | ## Load the raster | + | ## Load the the multiband raster file ''clip_SA2_2017-03-28_pca.tif'', which should be available in the [[Course data|course data]]. It contains the first 5 component as a result of a pricipal components analysis of a Sentinel-2 scene. |
| − | ## Open {{mitem|text=Vector --> Research tools --> regular points}}. | + | ## Open {{mitem|text=Vector --> Research tools --> regular points}}. Set the {{button|text=Input extent Layer}} to ''Use layer/canvas extent''. |
| − | ## | + | ## Enter the number 600 (meters) to {{button|text=Point spacing}}. |
| − | ## | + | ## Click {{button|text=Use point spacing)}} on. |
| − | ## Enter an output shapefile name and path by clicking {{button|text=Browse}} | + | ## Enter an output shapefile name ''systematic_grid.shp''and path by clicking {{button|text=Browse}}. |
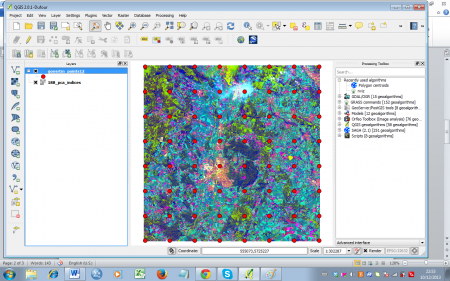
| − | ## Confirm with {{button|text= | + | ## Confirm with {{button|text=Run}}. Let the new layer be added to the [[TOC]] (figure '''A'''). |
| − | + | ||
# Buffering sample points | # Buffering sample points | ||
| + | |||
## Open {{mitem|text=Vector --> Geoprocessing tools --> Buffer}}. Select the generated points shapefile as input layer. | ## Open {{mitem|text=Vector --> Geoprocessing tools --> Buffer}}. Select the generated points shapefile as input layer. | ||
## Enter 200 (meter) as {{mitem|text=Buffer distance}}. | ## Enter 200 (meter) as {{mitem|text=Buffer distance}}. | ||
Revision as of 07:24, 24 April 2017
- A very important step in supervised image classification is the collection of training data. This is done in the training phase during which information on the spectral reflectance, it's variability and range for all classes that will be distincted by the classification is obtained. At first, we have to define the categories according to the objectives of the remote sensing study and the users's need. The training phase depends on previous knowledge acquired by field work or other sources of information like high-resolution satellite images or aerial photos. Furthermore, the reference information should be as acquired at the time of image acquisition if possible. One approach to collect reference data is the manual image interpretation which is done by image interpretersen who digitizing, delineate and identify training areas. There are different opinions to collect reference areas. In general, digital image classifiers, accuracy and quality measures require statistical based (probability) sampling. Therefore we need to define a sampling- and plot design. For the accuracy assessment we need an additional independent reference data set. The sample size should be large enough to divide the reference data into training and test data.
Working steps
- Generating sample points
- Load the the multiband raster file clip_SA2_2017-03-28_pca.tif, which should be available in the course data. It contains the first 5 component as a result of a pricipal components analysis of a Sentinel-2 scene.
- Open Vector --> Research tools --> regular points. Set the Input extent Layer to Use layer/canvas extent.
- Enter the number 600 (meters) to Point spacing.
- Click Use point spacing) on.
- Enter an output shapefile name systematic_grid.shpand path by clicking Browse.
- Confirm with Run. Let the new layer be added to the TOC (figure A).
- Buffering sample points
- Open Vector --> Geoprocessing tools --> Buffer. Select the generated points shapefile as input layer.
- Enter 200 (meter) as Buffer distance.
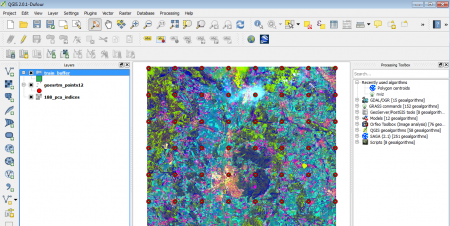
- Enter a file path and name, e.g. 188_pca_indices_buffer, confirm with OK and confirm the following dialogue to let the result be added to the project (figures B).
- To get an overview of the terrain, you may add a google sattelite layer
- Create a new shapefile layer
- Select Layer --> New --> New Shapefile Layer.
- As layer type, select Polygon. Click the Specify SRS button and select WGS 84/Pseudo Mercator (EPSG:3857).
- To add an attibute:
- For the attribute's name type (Class into the Name field of the New attribute section.
- Select Whole number as data type.
- Confirm with Add to attributes list.
- Confirm with OK and enter the path and name (e.g. Training) in the following menu.
- Select Layer --> New --> New Shapefile Layer.
- Digitizing areas
- Open the file digitizing_classes.pdf from the course data for a reference of landscape classes.
- Select the new shapefile in the TOC. Start the edit mode by clicking the Toggle editing button
 .
.
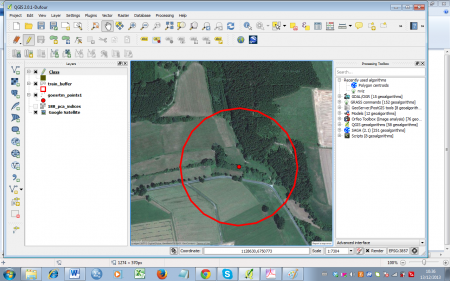
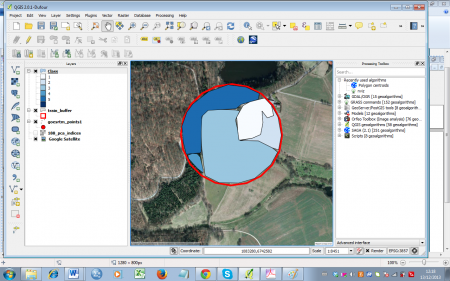
- Zoom in on a sample point (figure D). Click Add feature
 to start digitizing. Draw polygons according to the landscape classes. Simply click the desired point on the canvas to start. After selecting a second point, the third point will construct a triangle and each additional point will add another triangle to the geometry. Finish the geometry by right-clicking and entering the attributes in the appearing window (just use an increasing number for the ID). Take your time to get used to this way of digitizing -- you can always delete the last polygon by simply clicking Cancel in the attributes dialogue, or by selecting it
to start digitizing. Draw polygons according to the landscape classes. Simply click the desired point on the canvas to start. After selecting a second point, the third point will construct a triangle and each additional point will add another triangle to the geometry. Finish the geometry by right-clicking and entering the attributes in the appearing window (just use an increasing number for the ID). Take your time to get used to this way of digitizing -- you can always delete the last polygon by simply clicking Cancel in the attributes dialogue, or by selecting it  and deleting with the Delete selected
and deleting with the Delete selected  button. An example of a finished sample point can be seen in figure E.
button. An example of a finished sample point can be seen in figure E.