Per pixel supervised classification
From AWF-Wiki
(Difference between revisions)
(→Postprocessing) |
(→Postprocessing) |
||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
This application uses a the "Sieve" algorithm. | This application uses a the "Sieve" algorithm. | ||
| − | * In the search engine of Processing Toolbox, type {{typed|text=sieve}} and double click | + | * In the search engine of Processing Toolbox, type {{typed|text=sieve}} and double click Gdal > Raster analysis > ''' Sieve'''. |
* Define {{button|text=Input layer}} as an thematic raster map. | * Define {{button|text=Input layer}} as an thematic raster map. | ||
* Only raster polygons smaller than the size defined by {{button|text=Trheshold}} will be removed. Set to {{typed|text=2}} pixels. | * Only raster polygons smaller than the size defined by {{button|text=Trheshold}} will be removed. Set to {{typed|text=2}} pixels. | ||
| + | * Click checkbox {{button|text=Use 8-connectedness}} on. | ||
* Save the {{button|text=Sieved}} as '''svm_classification_sieve.tif'''. | * Save the {{button|text=Sieved}} as '''svm_classification_sieve.tif'''. | ||
* Click {{button|text=Run}}. | * Click {{button|text=Run}}. | ||
| Line 52: | Line 53: | ||
* Find the output ''svm_classification_sieve.tif'' in the QGIS map canvas. | * Find the output ''svm_classification_sieve.tif'' in the QGIS map canvas. | ||
* Right click on the layer ''svm_classification_sieve'' in the and select {{mitem|text=Properties --> Symbology --> Style --> Load Style}}. | * Right click on the layer ''svm_classification_sieve'' in the and select {{mitem|text=Properties --> Symbology --> Style --> Load Style}}. | ||
| − | * Select the style file '''rast_classified.qml'''. {{button|text=OK}} | + | * Select the style file '''rast_classified.qml'''. {{button|text=OK}} |
=Using OTB standalone= | =Using OTB standalone= | ||
Latest revision as of 06:41, 6 June 2022
Contents |
[edit] Using QGIS and OTB processing toolbox
- Using OTB version > 7.2.0, input vector file format of training data can be GeoPackage GPKG or ESRI Shapefile.
- The column containing class label needs to be an integer (whole number).
[edit] Training phase
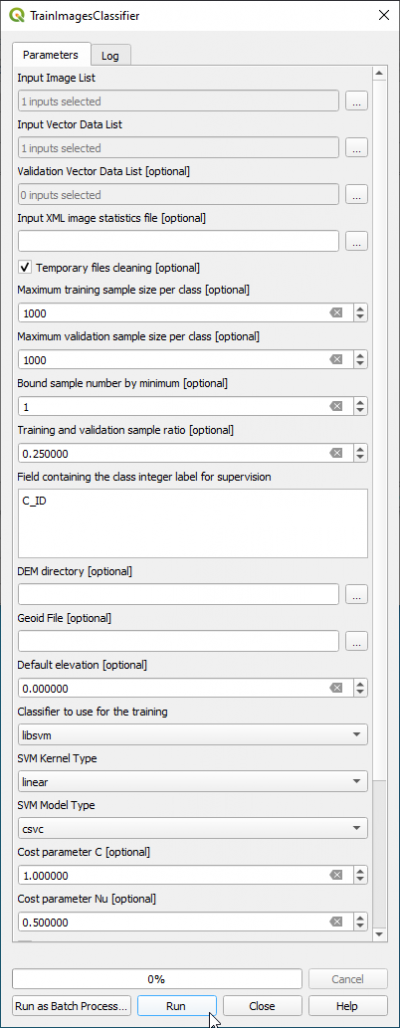
- In the search engine of Processing Toolbox, type TrainImages and open TrainImagesClassifer.
- In the Input Image List select one (or optional: several) multi-band raster (multispectral images).
- In the Input Vector Data List select a file containing training area polygons in format GPKG or SHP.
- If you do not have independent validation data: leave Validation Vector Data List empty.
- Bound sample number ba minimum: 1. The class with the minimum number of pixels determines the sample size of all other classes. Changing this value to 0 does not have an effect (current bug in QGIS3.16).
- Training and validation sample ratio: 0.25. This is a 4-fold cross-validation with split 0.75 per cent for training and 0.25 per cent for testing.
- Type Code in the Field containing the class integer label for supervision text field.
- As Classifier to use for training choose Support Vector Machine libsvm from the drop down list.
- The SVM Kernel Type is Linear.
- SVM Model Type is csvc
- Switch checkbox Parameters optimization off. The optimization results in a higher accuracy but takes much time (> 1 hour computation).
- In the Output model specify a model file: e.g. svm.model
- Click Run.
- Click on the Log tab and inspect the model quality measures: Precision, Recall, F-score and Kappa index.
[edit] Classification phase
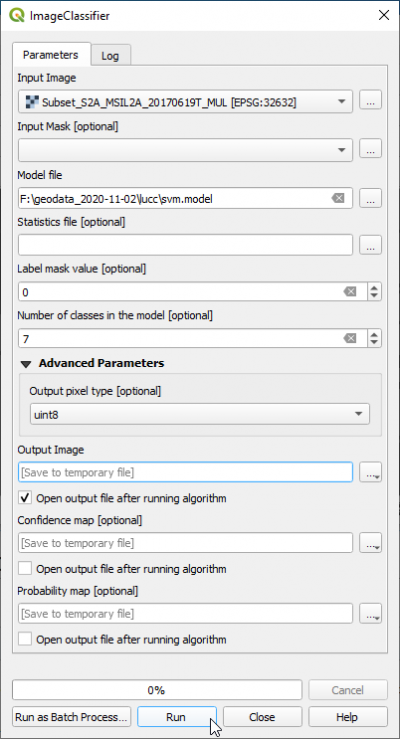
- In the search engine of Processing Toolbox, type ImageClassifier and double click ImageClassifier.
- Set an multiband image as Input image.
- Set Input _mask to blank (top of drop-down list).
- Set svm.model as Model file.
- Set the number of classes in your model: this is the number of unique classes in your training vector file.
- Set Output pixel type to uint16
- Save the Output image as svm_classification.tif.
- Uncheck Confidence map: Open output file after running algorithm.
- Uncheck Probability map: Open output file after running algorithm. Run.
- Find the output svm_classification.tif in the QGIS map canvas.
- Right click on the layer svm_classification and select Properties --> Symbology --> Style --> Load Style.
- Select the style file classified.qml. OK.
[edit] Postprocessing
"Sieve" removes raster polygons smaller than a provided threshold size (in pixels) and replaces them with the pixel value of the largest neighbour polygon. This is useful if you want to generalize a map and have a large amount of very small areas on your raster map
This application uses a the "Sieve" algorithm.
- In the search engine of Processing Toolbox, type sieve and double click Gdal > Raster analysis > Sieve.
- Define Input layer as an thematic raster map.
- Only raster polygons smaller than the size defined by Trheshold will be removed. Set to 2 pixels.
- Click checkbox Use 8-connectedness on.
- Save the Sieved as svm_classification_sieve.tif.
- Click Run.
- Find the output svm_classification_sieve.tif in the QGIS map canvas.
- Right click on the layer svm_classification_sieve in the and select Properties --> Symbology --> Style --> Load Style.
- Select the style file rast_classified.qml. OK
[edit] Using OTB standalone
[edit] Training phase
- Navigate in the Windows explorer to your Folder OTB-7.2.0-Win64. Double click the Windows-Batchdatei mapla to open Monteverdi Application Launcher.
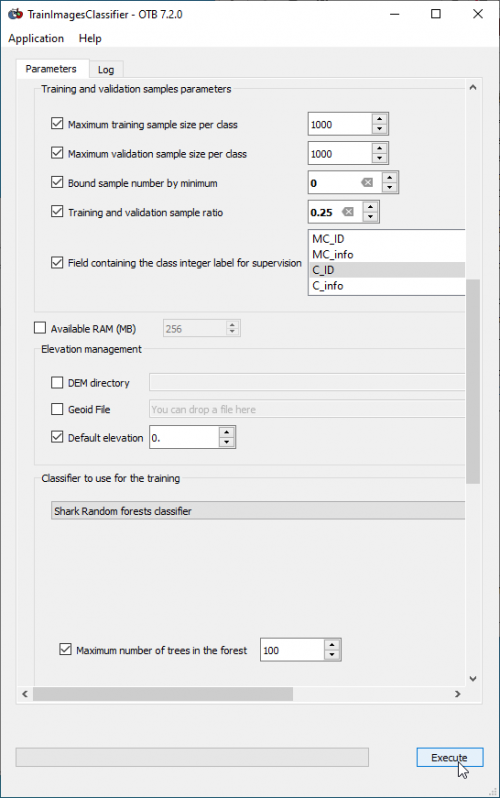
- In the search engine of mapla, type TrainImages and double click TrainImagesClassifer.
- In the Input Image List click on + and select a (or optional: several) multispectral images: Subset_S2A_MSIL2A_20170619T_MUL.tif .
- In the Input Vector Data List choose a vector polygon file with training areas in file format GPKG or SHP.
- In the Output model specify an output model file: e.g. lucc_rf.model
- In the Bound sample number by minimum field type 0.
- Set the training and validation sample ratio to 0.25.
- Mark C_ID in the Field containing the class integer label (C_ID refers to the column that contains the LUC code in the training and validation vector file).
- Choose Shark Random forests classifier from the drop down list as Classifier to use for the training.
- Check user defined Random seed and enter any positive integer value. This initializes a pseudorandom number generator which may be used to reproduce results.
- Click on Execute.
- Click on the Log tab and inspect the model quality measures: Precision, Recall, F-score and Kappa index.
[edit] Classification phase
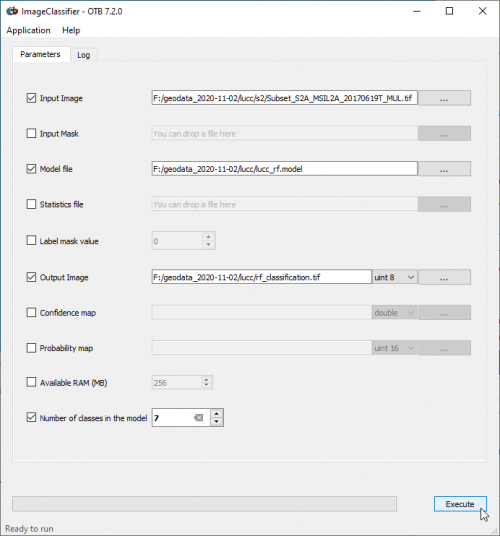
- In the search engine of mapla, type ImageClassifier and double click ImageClassifier
- Set Subset_S2A_MSIL2A_20170619T_MUL.tif as Input image.
- Set lucc_rf.model as Model file.
- Save the Output image as rf_classification.tif.
- Adjust the Number of classes in the model to the number of unique classes in the training vector file.
- Add rf_classification.tif to QGIS canvas.
- Download the style file classified.qml from Stud.IP.
- Right click on the layer rf_classification and select Properties --> Style --> Style --> Load Style.
- Select the style file classified.qml. OK.
[edit] Postprocessing
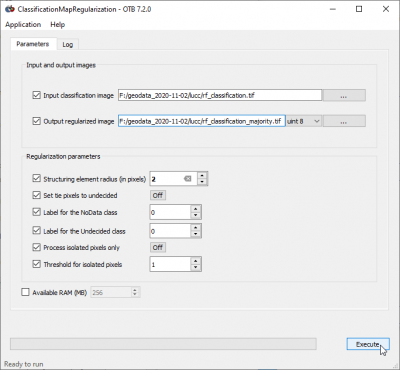
This application uses a majority with a circular structure element.
- In the search engine of mapla, type, regular and double click ClassifcationMapRegularization.
- As theInput classification image define the output raster file of the classification phase.
- Save the Output regularizd image as rf_classification_majority.tif.
- Set Structuring element radius to 2 pixels.
- Set Output pixel type to uint8.
- Click Execute.
- Add rf_classification_majority.tif to QGIS canvas.
- Download the style file classified.qml from Stud.IP.
- Right click on the layer rf_classification_majority and select Properties --> Style --> Style --> Load Style.
- Select the style file classified.qml. OK.