First-order texture
From AWF-Wiki
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
# Kurtosis | # Kurtosis | ||
The standard deviation of gray levels in a region in the neighborhood of a pixel can be calculated by a GRASS GIS modul: | The standard deviation of gray levels in a region in the neighborhood of a pixel can be calculated by a GRASS GIS modul: | ||
| + | Does currently not work in QGIS 3.4. | ||
* In the search engine of the Processing Toolbox, type '''neighbors''' and select '''r.neighbors''' under Raster of GRASS GIS 7 commands. | * In the search engine of the Processing Toolbox, type '''neighbors''' and select '''r.neighbors''' under Raster of GRASS GIS 7 commands. | ||
* Under the Parameters tab, select a single band file as input layer. | * Under the Parameters tab, select a single band file as input layer. | ||
Revision as of 19:19, 18 November 2018
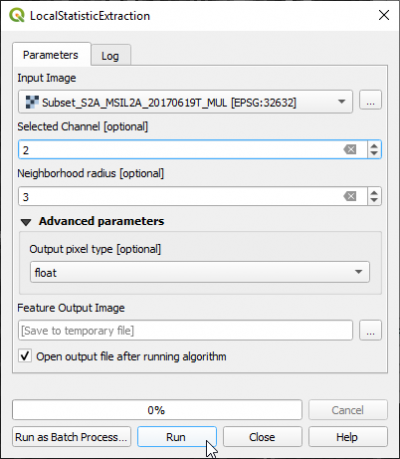
Local statistical moments (Mean, Variance, Skewness, Kurtosis) calculated on every pixel in the selected channel of the input image, over a specified neighborhood are called first-order textures.
- In the search engine of the Processing Toolbox, type Local Statistic and select LocalStatisticExtraction under Feature Extraction of OTB.
- Under the Parameters tab, select a single band or a multiband file as input layer.
- In case of a multiband file select the band number.
- Select 3 as Neighborhood radius in pixels.
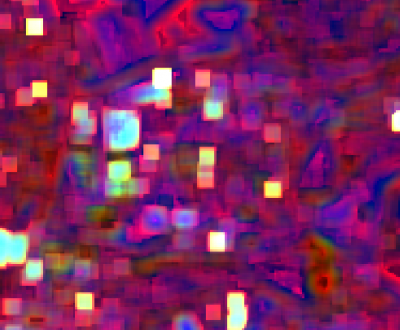
The output image (Fig. B) is a multiband with 4 statistical moments per band in the order:
- Mean
- Variance
- Skewness
- Kurtosis
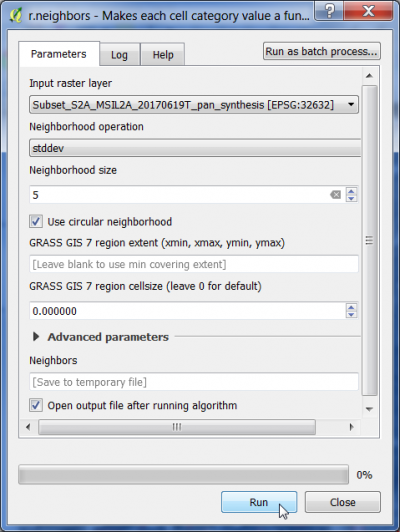
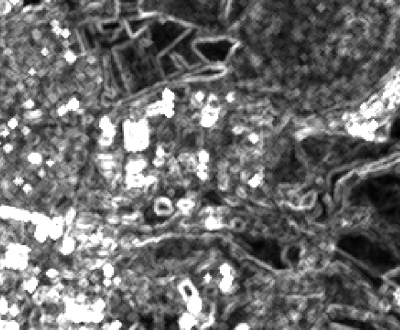
The standard deviation of gray levels in a region in the neighborhood of a pixel can be calculated by a GRASS GIS modul: Does currently not work in QGIS 3.4.
- In the search engine of the Processing Toolbox, type neighbors and select r.neighbors under Raster of GRASS GIS 7 commands.
- Under the Parameters tab, select a single band file as input layer.
- Select stddev from the drop-down list Neighborhood operation.
- Select an odd integer number as Neighborhood size in pixels.
- Tick Use circular neighborhood.