Cloud masking
From AWF-Wiki
(Difference between revisions)
(→Sentinel-2 cloud and cloud shadow masking) |
|||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
[[File:Qgis_cloud_dilate.png|300px]] | [[File:Qgis_cloud_dilate.png|300px]] | ||
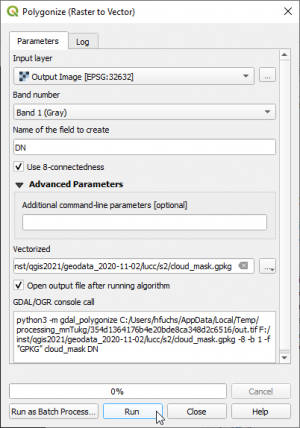
# Convert the Feature Output Imge from raster to vector format. {{mitem|text= Raster --> Conversion --> Polygonize}}. Select an output file name for vector polygons. | # Convert the Feature Output Imge from raster to vector format. {{mitem|text= Raster --> Conversion --> Polygonize}}. Select an output file name for vector polygons. | ||
| − | [[File:Qgis_cloud_polygonize.png | + | [[File:Qgis_cloud_polygonize.png|300px]] |
Revision as of 07:47, 13 November 2017
Sentinel-2 cloud and cloud shadow masking
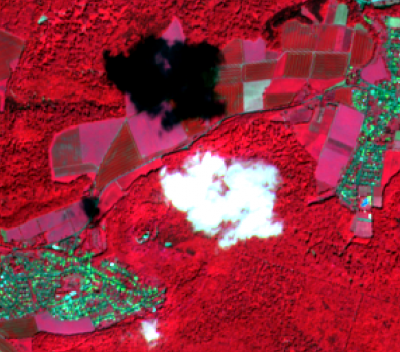
The exclusion of clouds and cloud shadow is an important processing step which is usually done in an early preprocessing stage. The Sentinel-2 products are annotated with Quality Indicators (QI_DATA). In the Level 2A product you may find a file in the folder QI_DATA with the extension _CLD_20m.jp2 (data type: 8bit unsigned integer, spatial resolution 20m) which might be used for masking clouds. The data range is from 0 for high confidence clear sky to 100 for high confidence cloudy (for more details see L2A Product Definition Document).
- Load a multiband Sentinel-2 satellite image (Level 2-A product) Changing Raster Layer Style to display a true color and a false color composite.
- Zoom in to a cloudy part of the image and compare the extent of cloud and cloud shadow in both composites. Which composite is better for displaying clouds?
- The original single band cloud quality indicator band is included in this specifc multiband file as band No. 13. Follow Split stack to extract this band.
- Overlay the QI Cloud band on top of the color composites. Use the Identify Feature Tool for requesting pixel values of the QI band file inside a cloud. Which values represent clouds?
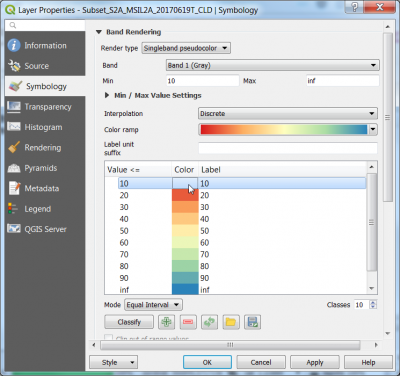
- In (Layer Properties Style load Load the full data range (minimum/maximum values) ). Then change the Style to a Pseudocolor map with interpolation discrete and 10 equal interval classes as shown in the screenshot.
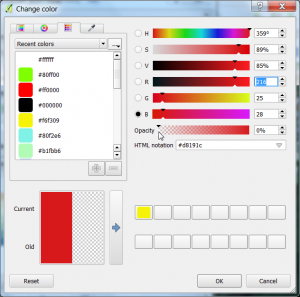
- Double click on a color field of some classes (Layer Properties Style) to open the change color window. Change the opacity from 100% to 0%. Find the best threshold for clouds.
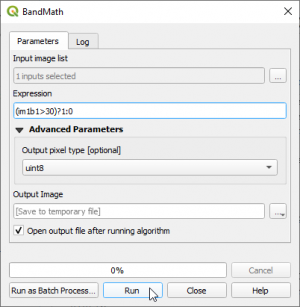
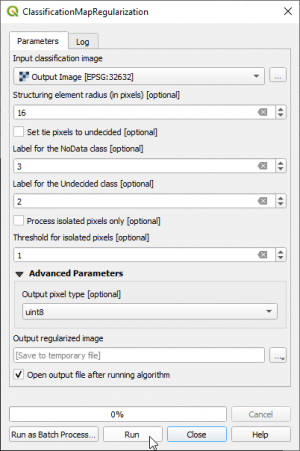
- Create a binary cloud mask (bitmask) where clouds = 1 and non-clouds = 0. Use the Processing tool Orfeo Toolbox --> Miscellaneous --> Band Math. Tick the single band QI layer in the Input Image list list. You may write a conditional ifelse expression using lazy operators. Type into the Expression field: (im1b1>30)?1:0. If pixel values of band 1 of multiband image 1 are larger than 30 then replace with 1 otherwise replace with 0. Mark the output layer in the TOC and click
 to stretch the histogram to view extents.
to stretch the histogram to view extents.
- Apply a circular majority filter with a radius of 7 pixels. Open the Processing tool SAGA Toolbox --> Raster filter --> Majority filter. The input Grid is the Output image of the band math operation step. Change the Search mode to Circle with an radius of 7 pixels. Mark the 'Filtered Grid in the TOC and click
 to stretch the histogram to view extents.
to stretch the histogram to view extents.
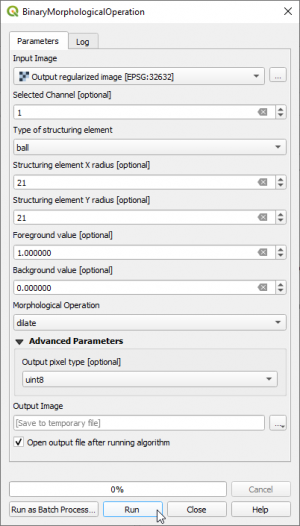
- Open the Processing tool Ordeo Toolboy --> Feature Extraction --> BinaryMorphologicalOperation (dilate). Choose the Filtered Grid as input image. The structuring element type is ball with a radius of 9 pixels. Mark the 'Feature Output Image in the TOC and click
 to stretch the histogram to view extents.
to stretch the histogram to view extents.
- Convert the Feature Output Imge from raster to vector format. Raster --> Conversion --> Polygonize. Select an output file name for vector polygons.