Spectral indices
From AWF-Wiki
(Difference between revisions)
(→Vegetation index using the Raster Calculator) |
(→Spectral indices using Processing Toolbox) |
||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
* Click {{button|text=Help}}to find definitions of available spectral indices in three categories (vegetation, water, soil) and relevant channels of the input multiband image. | * Click {{button|text=Help}}to find definitions of available spectral indices in three categories (vegetation, water, soil) and relevant channels of the input multiband image. | ||
| − | [[File:Qgis_radio_index.png|left| | + | [[File:Qgis_radio_index.png|left|400px]] |
| + | |||
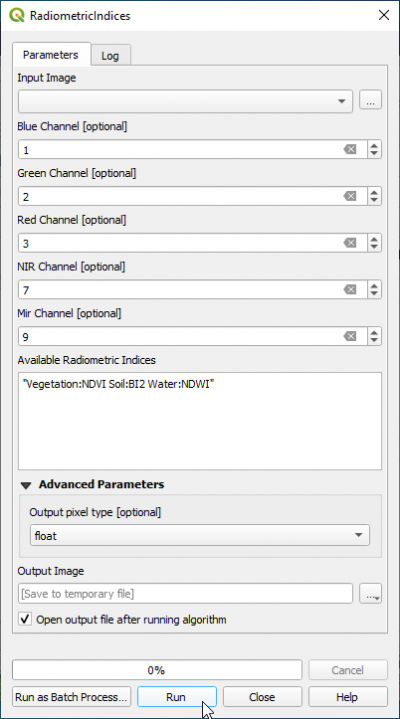
| + | If you want to create a multiband spectral index file click {{button|text=Run}} and see the list of available radiometric indices. | ||
| + | * In the text field ''Available Radiometric Indices'' type with apostrophs:{{typed|text="Vegetation:NDVI Water:NDWI Soil:BI2"}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Qgis_radiometric_composite.png|left|400px]] | ||
| + | |||
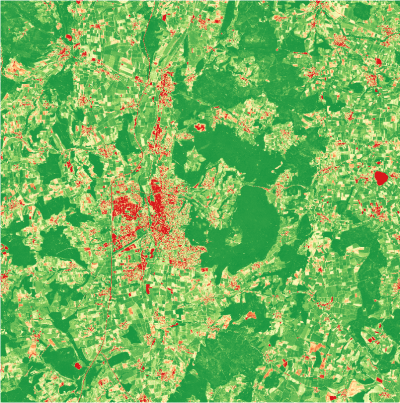
* Display the output single band spectral index image in the canvas ('''Fig. B'''). | * Display the output single band spectral index image in the canvas ('''Fig. B'''). | ||
Revision as of 14:00, 16 November 2019
Vegetation index using the Raster Calculator
- Click the Open Data Source Manager
 and then Add raster layer
and then Add raster layer  and select the file /geodata/lucc/s2/Subset_S2A_MSIL2A_20170619T_MUL.tif.
and select the file /geodata/lucc/s2/Subset_S2A_MSIL2A_20170619T_MUL.tif.
- Check the rank and spectral range of bands in the multiband file (e.g. see table Changing Raster Layer Style).
- After clicking Open, the raster layer appears in the QGIS canvas.
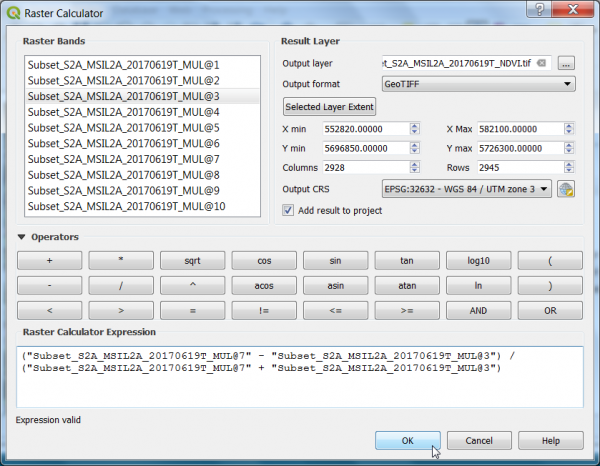
- Click Raster --> Raster calculator.
- A powerful normalization is realized by the normalized difference vegetation index that forms the basis of most vegetation indices $NDVI = (Nir - Red) / (Nir + Red)$. It can be implemented using Raster Calculator as seen in the following screenshot:
- Define path and file name of the output layer. OK.
- Map visualization: Open the raster layer properties by right-clicking the ndvi raster in the TOC selecting Properties, or by simply double clicking.
- Select the Style tab. Under Render type select Singleband pseudocolor.
Spectral indices using Processing Toolbox
A convenient module for calculating one or several spectral indices at the same time can be found in the QGIS processing toolbox.
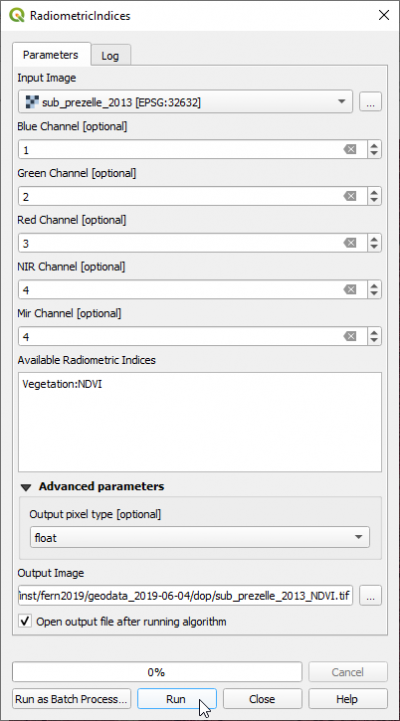
- Type Radiometric into the search field and find the OTB --> Feature Extraction --> Radiometric Indices) tool.
- Open it with a double click.
- Assign the bands in the multiband file to the correct spectral sensitivity.
- in the text field Available Radiometric Indices type:Vegetation:NDVI
- Click Run.
- Click Helpto find definitions of available spectral indices in three categories (vegetation, water, soil) and relevant channels of the input multiband image.
If you want to create a multiband spectral index file click Run and see the list of available radiometric indices.
- In the text field Available Radiometric Indices type with apostrophs:"Vegetation:NDVI Water:NDWI Soil:BI2"
- Display the output single band spectral index image in the canvas (Fig. B).